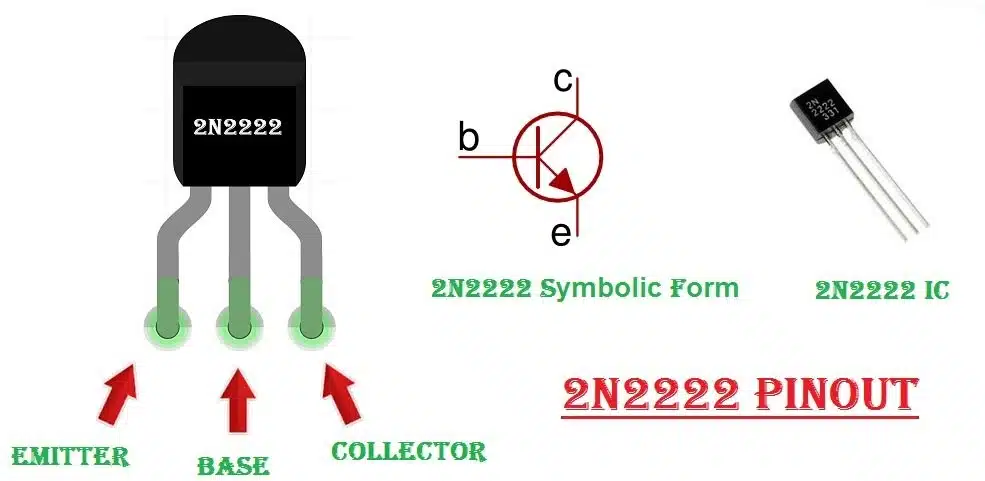
The 2N2222 and 2N2222A transistors serve as versatile components in electronic circuits. Both belong to the NPN bipolar junction category, but the 2N2222A offers enhanced electrical specifications, such as higher gain and speed. These transistors excel in switching, amplification, and sensor interface applications, making them essential in Discrete Semiconductor Products for modern designs.
Key Takeaways
-
The 2N2222A transistor works faster and amplifies better than the 2N2222.
-
Use the 2N2222 for simple jobs like turning on LEDs or relays. The 2N2222A is better for accurate amplifying and quick switching.
-
Check your circuit’s needs, like power and speed, to pick the right transistor for best results.
Differences Between 2N2222 and 2N2222A
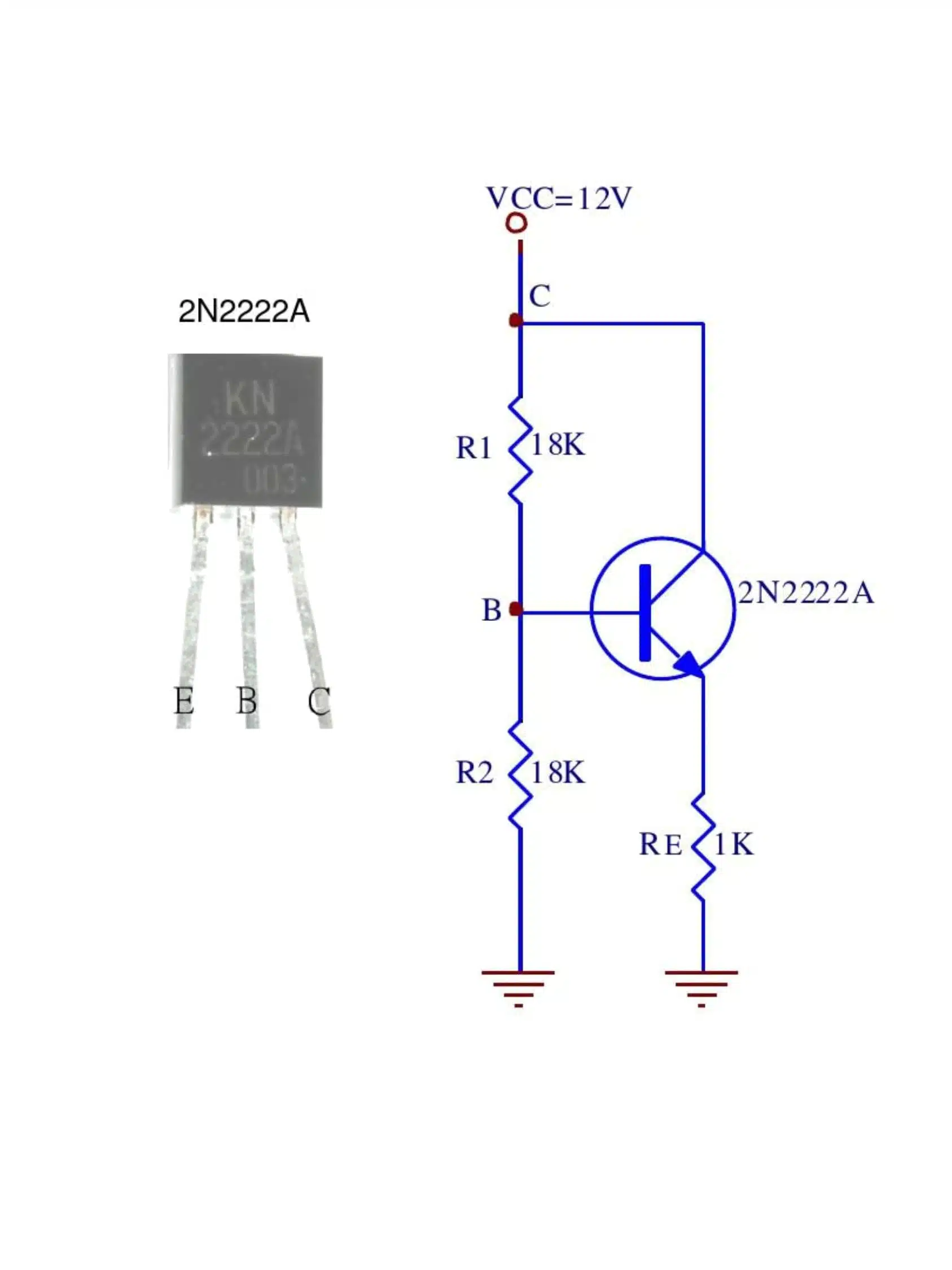
Electrical Specifications
The 2N2222 and 2N2222A transistors share many similarities in their electrical characteristics, but subtle differences set them apart. Both transistors are NPN bipolar junction types, designed for low-power switching and amplification. However, the 2N2222A typically offers slightly better performance in terms of gain and speed.
For instance, the 2N2222A often has a higher current gain (hFE) at specific operating points, making it more efficient in amplification circuits. Additionally, the 2N2222A can handle higher frequencies, which makes it suitable for high-speed switching applications. According to the datasheet, both transistors can handle a maximum collector current of 800 mA and a collector-emitter voltage of 30 V. These specifications make them versatile for various circuit designs.
Packaging and Material
The packaging and material of these transistors also differ slightly. The 2N2222 is commonly available in a TO-18 metal can package, which provides excellent thermal conductivity and durability. This makes it ideal for applications where heat dissipation is a concern.
On the other hand, the 2N2222A is often found in a TO-92 plastic package, which is more cost-effective and lightweight. While the TO-92 package may not offer the same level of heat dissipation as the TO-18, it is sufficient for most low-power applications. The choice between these two packages depends on the specific requirements of the circuit, such as thermal management and physical space constraints.
Circuit Performance
When comparing circuit performance, the 2N2222A generally outperforms the 2N2222 in high-frequency and high-gain applications. Its improved electrical specifications allow it to operate more efficiently in circuits requiring rapid switching or precise signal amplification.
For example, in oscillator circuits or pulse-width modulation (PWM) controllers, the 2N2222A’s higher speed ensures better performance. However, the 2N2222 remains a reliable choice for general-purpose applications, such as driving relays or LEDs, where extreme performance is not critical.
Both transistors excel in small-signal amplification and switching tasks, but the 2N2222A’s enhanced capabilities make it a preferred choice for demanding applications. Designers should evaluate their circuit’s specific needs to determine which transistor is the better fit.
Choosing the Right Transistor
Circuit Requirements
Selecting the correct transistor for a circuit depends on several factors, including the circuit’s power, frequency, and gain requirements. For instance, circuits requiring high-speed switching benefit from npn transistors like the 2n2222 transistor or its variant, the 2n2222A. These transistors excel in applications where rapid on/off control is essential.
The working principle of transistors involves three states: cutoff, amplification, and saturation. In the cutoff state, the transistor acts as an open switch, making it ideal for digital circuits. In the amplification state, it provides linear current gain, which is crucial for signal amplification. Finally, in the saturation state, the transistor functions as a closed switch, suitable for high-current applications.
The table below highlights benchmarks for choosing between relays and transistors based on circuit needs:
|
Application Area and Specification |
Relay |
Transistor |
|---|---|---|
|
Power Level |
Handles very high voltages and currents. |
Power transistors manage up to ~100 V and dozens of amps. |
|
Load Type |
Supplies power to various loads. |
Requires careful design to avoid saturation. |
|
Switching Frequency |
Slow switching, not suitable for frequent events. |
Operates at high frequencies (~100 kHz to ~2 GHz). |
|
ON-State Resistance |
Very low, equal to DC resistance. |
Down to ~mOhm for large power MOSFETs. |
Understanding these metrics helps designers determine whether a 2n2222 transistor or another component is the best fit for their circuit.
Use Cases for 2N2222 Transistor
The 2n2222 transistor is a versatile component in low-power circuits. Its robust design and TO-18 metal can package make it suitable for applications requiring durability and heat dissipation. Common use cases include:
-
Switching Applications: The 2n2222 transistor drives relays, LEDs, and small motors effectively. It also supports TTL-level interfacing in digital circuits.
-
Amplification: It amplifies small signals in audio circuits and preamplifiers. Its moderate gain range ensures reliable performance without excessive noise.
-
Oscillator Circuits: The 2n2222 transistor performs well in RC or LC oscillator designs, enabling pulse generation.
-
Sensor Interfaces: It amplifies signals from analog sensors, making it ideal for sensor-based circuits.
This transistor’s reliability and thermal efficiency make it a preferred choice for general-purpose applications.
Use Cases for 2N2222A Transistor
The 2n2222A transistor offers enhanced performance, making it suitable for demanding applications. Its higher gain and speed allow it to excel in circuits requiring precision and efficiency. Typical use cases include:
-
High-Speed Switching: The 2n2222A transistor operates efficiently in circuits with rapid switching requirements, such as PWM controllers and inverter circuits.
-
Signal Amplification: Its higher gain range makes it ideal for amplifying weak signals in radios and precision audio systems.
-
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM): The 2n2222A transistor controls power delivery in PWM circuits, ensuring smooth operation of DC motors and heaters.
-
Darlington Pair Circuits: When paired with another transistor, the 2n2222A achieves higher gain, making it suitable for high-performance amplification.
The 2n2222A transistor’s TO-92 plastic package also offers a lightweight and cost-effective solution for low-power applications. Its versatility and improved specifications make it a valuable component in modern circuit designs.
Suppliers and Pricing in 2025
Reliable Suppliers of Discrete Semiconductor Products
In 2025, sourcing reliable discrete semiconductor products remains crucial for circuit designers. Several manufacturers and distributors specialize in providing high-quality npn transistors like the 2N2222 and 2N2222A. ON Semiconductor, Microsemi, and Central Semiconductor are among the leading manufacturers. These companies offer datasheets and technical support to ensure proper integration into circuits.
For purchasing, distributors such as Digi-Key, Mouser Electronics, and Newark provide a wide range of options. They stock both TO-18 and TO-92 packages, along with substitutes like the PN2222A and MMBT2222A. These distributors also cater to bulk orders, making them ideal for large-scale projects. Selecting a trusted supplier ensures access to genuine components and minimizes the risk of counterfeit semiconductors.
Price Trends for 2N2222 Transistor
The pricing of npn transistors like the 2N2222 has remained stable over the years. In 2025, the average cost for a single 2N2222 transistor ranges between $0.10 and $0.50, depending on the package and manufacturer. The 2N2222A, with its enhanced specifications, typically costs slightly more, averaging $0.20 to $0.70 per unit.
Substitutes such as the PN2222A and MMBT2222A offer cost-effective alternatives, especially for low-power applications. Bulk purchases often reduce costs significantly, making them a preferred option for manufacturers and hobbyists alike. Monitoring price trends helps designers plan budgets effectively while ensuring access to high-quality semiconductors.
Bulk Purchase Tips
Buying npn transistors in bulk can save costs and ensure a steady supply for projects. Designers should consider the following tips:
-
Compare Suppliers: Evaluate prices and shipping options from multiple distributors.
-
Check Substitutes: Consider alternatives like the MMBT2222A or BC337 for cost savings.
-
Verify Authenticity: Purchase from authorized distributors to avoid counterfeit semiconductors.
-
Plan Ahead: Anticipate future needs to take advantage of bulk discounts.
These strategies help reduce costs while maintaining the quality and reliability of discrete semiconductor products.
The 2N2222 and 2N2222A transistors differ in electrical specifications, packaging, and circuit performance. Choosing the right transistor depends on circuit requirements and budget constraints. Designers should prioritize performance for demanding applications or opt for cost-effective solutions for general-purpose use.
Tip: Evaluate circuit needs carefully to ensure optimal functionality and cost efficiency.
What is the main difference between the 2N2222 and 2N2222A transistors?
The 2N2222A offers higher gain and speed compared to the 2N2222. It also comes in a TO-92 plastic package, while the 2N2222 uses a TO-18 metal can.
Can the 2N2222A replace the 2N2222 in all circuits?
Yes, the 2N2222A can replace the 2N2222 in most circuits. However, designers should verify the circuit’s thermal and packaging requirements before substitution.
Which transistor is better for high-frequency applications?
The 2N2222A performs better in high-frequency applications due to its improved speed and gain. It is ideal for oscillators and pulse-width modulation circuits.
See Also
M30280FAHP: A Dependable Option For Medical Integrated Circuits
IRF820: A Versatile N-Channel MOSFET For Power Applications
Reasons To Select Coilcraft XPL2010 For VRM And VRD
Understanding MC9S12DJ256MFUE Specs For Automotive Uses
Enhancing MC9S12XEP100 And MC9S12XS128 Performance Using NXP

