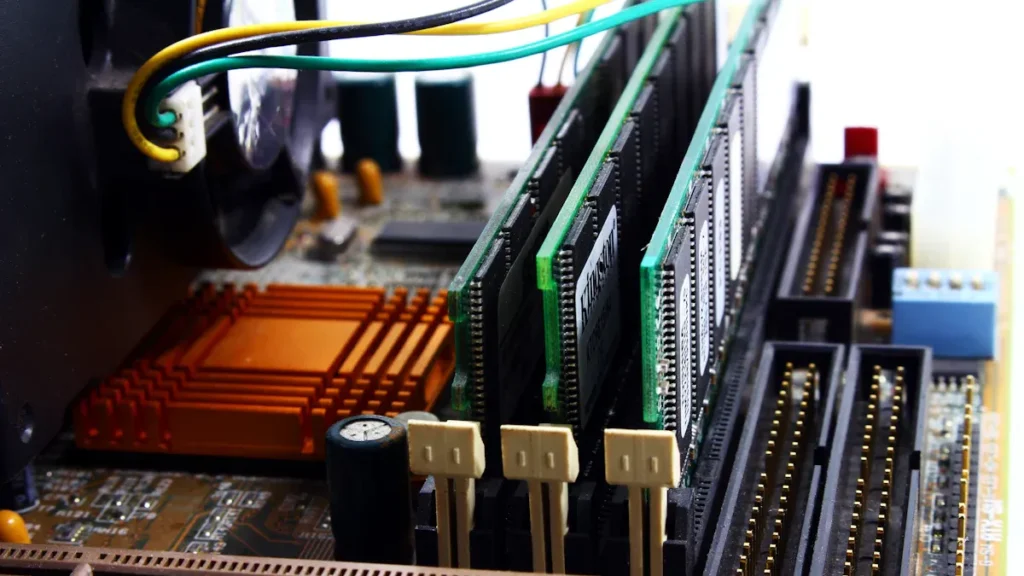
The evolution of RAM technology has brought significant changes in performance and efficiency. DDR4 vs. DDR5 showcases a leap in speed, bandwidth, and capacity, making DDR5 ideal for demanding tasks. However, DDR4 remains a reliable choice for many users due to its compatibility and affordability. Selecting the right RAM depends on the device it serves. For desktops, high-performance desktops, or servers, the choice impacts multitasking, gaming, or data processing. DDR4 and DDR5 memory (RAM) parts commonly used in desktops highlight this difference. Consulting an electronic components distributor ensures compatibility with your system.
Key Takeaways
-
DDR5 RAM is faster and better for gaming and creating content.
-
DDR4 RAM is cheaper and works well for simple tasks like browsing or typing.
-
You cannot use DDR4 and DDR5 together in one computer. Check your motherboard before upgrading.
-
If you need high speed, DDR5 is a good choice for the future. DDR4 is good for older computers or saving money.
-
Think about your needs. DDR5 is great for heavy tasks, while DDR4 works fine for regular use.
What Are DDR4 and DDR5 RAM?
Overview of DDR4 RAM
DDR4 RAM, introduced in 2014, remains a widely used memory standard for desktops, laptops, and servers. It offers reliable performance with base frequencies starting at 2133 MHz and overclocked speeds reaching up to 5333 MHz. Its bandwidth ranges from 17 GB/s to 21.3 GB/s, making it suitable for multitasking and moderate workloads. DDR4 operates at a voltage of 1.2V, ensuring energy efficiency for most systems. While its latency is lower compared to DDR5, it compensates with consistent performance across various applications.
DDR4 RAM modules typically support up to 32GB per stick, providing adequate capacity for gaming, content creation, and enterprise tasks. The motherboard controls power management, which simplifies system design but limits advanced features. Despite its age, DDR4 remains relevant due to its affordability and compatibility with older systems.
Overview of DDR5 RAM
DDR5 RAM, launched in 2021, represents a significant leap in memory technology. It starts with a base frequency of 4800 MHz and can exceed 8000 MHz when overclocked. With bandwidth improvements reaching over 38 GB/s, DDR5 delivers faster data transfer rates, ideal for high-performance computing. Its voltage requirement of 1.1V enhances power efficiency, while the inclusion of on-module Power Management Integrated Circuits (PMIC) ensures better control and stability.
DDR5 RAM modules support up to 128GB per stick, making them suitable for memory-intensive tasks like AI workloads and virtualization. Built-in error correction (ECC) improves reliability, especially for enterprise servers. Although DDR5 has higher latency, its speed compensates for this, ensuring smooth operation in demanding environments.
Importance of RAM in Desktops, Laptops, and Servers
RAM plays a crucial role in optimizing system performance. It acts as short-term memory, enabling smooth multitasking and application execution. In desktops, DDR4 RAM provides sufficient capacity for gaming and everyday use, while DDR5 RAM enhances performance for high-end tasks like 3D rendering. Laptops benefit from DDR5’s energy efficiency, extending battery life during intensive workloads.
Servers rely heavily on RAM for scalability and reliability. DDR5 memory, with its higher density and bandwidth, supports virtualization and cloud hosting more effectively than DDR4. Monitoring RAM usage and managing applications that consume excessive memory ensures optimal performance across all devices.
Key Differences Between DDR4 and DDR5

Performance: Speed, Bandwidth, and Latency
DDR4 vs. DDR5 highlights significant differences in speed, bandwidth, and latency. DDR4 RAM starts at 1600 MHz and can reach up to 5000 MHz with overclocking. DDR5 RAM begins at 3200 MHz and peaks at 6400 MHz, offering faster data transfer rates. Higher speeds in DDR5 improve memory bandwidth, allowing systems to handle more data simultaneously.
Latency, however, presents a trade-off. DDR4 RAM has a lower latency of 16, meaning it responds faster to CPU requests. DDR5 RAM, with a latency of 32, compensates for this delay through its higher speeds. Benchmark tests reveal mixed results. Cinebench R23 shows similar performance for DDR4 and DDR5, with high-end DDR5 offering slight improvements. Blender benchmarks indicate a 6.5% performance increase when upgrading from DDR4-3200 to DDR5-6000. In 7-Zip compression tests, DDR5 demonstrates a 61% speed boost over DDR4.
🧠 Tip: Gamers and content creators benefit most from DDR5’s higher bandwidth, while everyday users may find DDR4 sufficient for their needs.
Capacity and Density Improvements
DDR5 RAM introduces substantial advancements in memory capacity and density. DDR4 RAM modules support a maximum density of 16 Gb per die, resulting in a total capacity of 32 GB per module. DDR5 RAM increases density to 64 Gb per die, enabling modules to reach 128 GB. This improvement makes DDR5 ideal for memory-intensive tasks like virtualization and AI workloads.
|
Feature |
DDR5 |
DDR4 |
|---|---|---|
|
64 Gb |
16 Gb |
|
|
Total Capacity |
128 GB |
32 GB |
Micron’s DDR5 memory demonstrates up to five times the performance of DDR4 in deep learning applications. These advancements ensure DDR5 can handle larger datasets and complex computations more efficiently than DDR4.
💡 Note: Enterprise servers and workstations benefit most from DDR5’s increased memory capacity, while DDR4 remains a cost-effective option for smaller workloads.
Power Consumption and Efficiency
DDR5 RAM improves power efficiency by reducing voltage requirements. DDR4 RAM operates at 1.2V, while DDR5 RAM lowers this to 1.1V. This reduction enhances energy savings, especially in laptops and servers. DDR5 also integrates Power Management Integrated Circuits (PMIC) directly onto the module. This feature allows better control over power distribution, reducing heat generation and improving stability.
DDR5’s efficiency makes it suitable for devices requiring prolonged operation, such as laptops and embedded systems. Servers benefit from DDR5’s ability to handle high workloads without excessive power consumption. DDR4 RAM, while less efficient, remains a reliable choice for systems prioritizing affordability over energy savings.
🔋 Tip: For users seeking energy-efficient solutions, DDR5 RAM offers long-term benefits, especially in high-performance environments.
Compatibility with Existing Systems
When comparing ddr4 vs. ddr5, compatibility becomes a critical factor for users upgrading or building new systems. DDR4 and DDR5 RAM are not interchangeable due to differences in architecture and physical design. Each type requires a motherboard specifically designed to support it. For instance, a ddr5 compatible motherboard features a unique DIMM slot configuration that prevents DDR4 modules from being installed.
DDR4 RAM works seamlessly with most systems released before 2021. Its widespread adoption ensures compatibility with a vast range of motherboards, making it a reliable choice for users upgrading older desktops or laptops. However, DDR5 RAM demands newer platforms, as its advanced features like on-module power management and higher bandwidth require updated hardware.
Manufacturers like Intel and AMD have introduced chipsets that support DDR5, but these often exclude DDR4 compatibility. This shift forces users to carefully evaluate their system requirements before making a decision. Gamers and professionals building high-performance desktops should prioritize motherboards that align with their chosen RAM type.
💡 Tip: Always verify motherboard specifications to ensure compatibility with DDR4 or DDR5 RAM. Upgrading to DDR5 may also require a CPU that supports the latest memory standards.
Thermal Management and Heat Dissipation
Thermal management plays a vital role in maintaining system stability and performance. DDR4 and DDR5 RAM differ in how they handle heat generation and dissipation. DDR4 RAM operates at 1.2V, which produces less heat compared to older memory standards. Its thermal output remains manageable in most systems, even during extended workloads.
DDR5 RAM, despite its higher speeds and bandwidth, improves thermal efficiency by reducing voltage to 1.1V. Additionally, DDR5 modules integrate Power Management Integrated Circuits (PMIC) directly onto the RAM stick. This feature optimizes power distribution, reducing heat buildup and enhancing stability under heavy loads.
Heat spreaders and cooling solutions further improve thermal performance for both DDR4 and DDR5. High-performance DDR5 modules often include advanced heat spreaders to dissipate heat more effectively. These enhancements make DDR5 suitable for demanding applications like gaming, AI workloads, and virtualization.
🔥 Note: Proper airflow and cooling are essential for systems using DDR5 RAM, especially when overclocking. Users should consider investing in quality cooling solutions to prevent thermal throttling.
Advantages and Disadvantages of DDR4 and DDR5
Pros and Cons of DDR4 RAM
DDR4 RAM offers several advantages that make it a reliable choice for many users. It delivers improved performance compared to DDR3, with faster transfer rates and lower latency. This makes it suitable for multitasking and moderate workloads. Its lower power consumption reduces energy costs and extends battery life, especially in laptops. DDR4 also supports higher module densities, allowing up to 32 GB per stick, which enhances multitasking capabilities. Features like temperature sensing and voltage monitoring improve reliability, ensuring stable operation in various environments.
However, DDR4 has some limitations. It is slower than DDR5, which offers significantly faster transfer rates and higher bandwidth. DDR4 also has limited density options, with fewer high-capacity modules available. While it remains compatible with most systems released before 2021, it lacks the advanced features of DDR5, such as on-module power management.
💡 Note: DDR4 remains the best ddr4 ram option for users seeking affordability and compatibility with older systems.
Pros and Cons of DDR5 RAM
DDR5 RAM introduces cutting-edge features that enhance performance and efficiency. It offers significantly faster transfer rates and higher bandwidth compared to DDR4, making it ideal for high-performance computing tasks. DDR5 consumes less power despite its higher speeds, thanks to its reduced voltage requirement of 1.1V. It supports much higher module densities, with capacities reaching up to 128 GB per stick. Enhanced error correction and stability features, such as built-in ECC, improve reliability, especially in enterprise servers.
Despite its advantages, DDR5 has some drawbacks. It is generally more expensive than DDR4, which may deter budget-conscious users. Compatibility issues arise as DDR5 requires new hardware components, including motherboards and CPUs designed for its architecture. BIOS updates may also be necessary to ensure proper functionality. Additionally, DDR5’s latency is higher than DDR4, although its increased speed compensates for this in most scenarios.
|
Feature |
DDR4 |
DDR5 |
|---|---|---|
|
Advantages |
||
|
Improved Performance |
Faster than DDR3, lower latency |
Significantly faster than DDR4 |
|
Lower Power Consumption |
Uses less electricity than DDR3 |
Consumes less power despite higher speeds |
|
Increased Capacity |
Supports higher module densities |
Supports much higher module densities |
|
Better Reliability |
Built-in features for stability |
Enhanced error correction and stability |
|
Disadvantages |
||
|
Slower Than DDR5 |
Yes |
N/A |
|
Limited Density Options |
Fewer high-density modules available |
N/A |
|
More Expensive |
N/A |
Generally more expensive than DDR4 |
|
Compatibility Issues |
N/A |
Requires new hardware components |
|
May Require BIOS Updates |
N/A |
May need BIOS updates |
🧠 Tip: DDR5 is the best choice for users seeking future-proof memory solutions, especially for high-performance desktops and servers.
Use Cases for DDR4 and DDR5 Memory (RAM) Parts Commonly Used in Desktops

For Gamers: Performance and FPS Gains
Gamers rely on RAM to achieve smooth gameplay and higher frame rates. DDR4 RAM remains a capable choice for most gaming setups, offering reliable performance at an affordable price. However, DDR5 RAM provides noticeable improvements in gaming benchmarks, especially for modern titles optimized for higher memory bandwidth.
-
In Assassin’s Creed Mirage, DDR5 delivers a 13% boost in 1% lows and a 7% increase in average frame rates at 1080p.
-
Cyberpunk 2077: Phantom Liberty shows a 9% speed advantage for DDR5 at 1080p.
-
Watch Dogs: Legion benefits from DDR5 with up to 14% better performance at 1080p.
-
Baldur’s Gate 3 sees a 20 fps improvement, translating to a 14% gain at both 1080p and 1440p.
DDR5’s faster speeds and higher bandwidth make it ideal for gamers seeking smoother gameplay and reduced stuttering during intense scenes. Popular DDR5 modules like the G.Skill Trident Z5 DDR5-6400 and Corsair Vengeance DDR5-6000 are widely used for high-performance gaming rigs.
🎮 Tip: Gamers building new systems should prioritize DDR5 for future-proofing, while DDR4 remains a cost-effective option for older platforms.
For Content Creators: Handling Creative Workloads
Content creators depend on RAM to handle memory-intensive tasks like video editing, 3D rendering, and simulations. DDR4 RAM supports most creative workflows, offering sufficient capacity and speed for moderate workloads. However, DDR5 RAM excels in demanding applications due to its higher clock speeds and bandwidth.
-
DDR5 enables faster data access and application launches, reducing lag during real-time editing of large media files.
-
For 3D rendering and simulations, DDR5’s increased bandwidth enhances multitasking and speeds up complex computations.
-
Popular DDR5 modules like the Kingston Fury Beast DDR5-5200 and G.Skill Trident Z5 DDR5-6400 are favored by professionals for their reliability and performance.
Content creators using software like Adobe Premiere Pro or Blender benefit from DDR5’s ability to load large datasets quickly and efficiently. While DDR4 remains a viable option for budget-conscious users, DDR5 offers significant productivity gains for those handling advanced creative workloads.
💡 Note: Professionals working with high-resolution media or complex simulations should consider DDR5 for its superior performance.
For Enterprise Servers: Scalability and Reliability
Enterprise servers require RAM that ensures scalability and reliability for critical workloads. DDR4 RAM continues to serve small to mid-sized workloads effectively, offering stability and affordability. However, DDR5 RAM introduces features that make it ideal for modern data centers and large-scale applications.
-
DDR5 supports higher module densities, with capacities reaching up to 128 GB per stick, enabling better virtualization and cloud hosting.
-
Built-in error correction (ECC) in DDR5 improves reliability, reducing downtime for enterprise servers.
-
Popular DDR5 server modules like the Samsung DDR5-4800 ECC RDIMM and Micron DDR5-4800 ECC RDIMM are widely adopted in next-gen server platforms.
Servers running AI and machine learning workloads benefit from DDR5’s enhanced bandwidth and efficiency. DDR4 remains a cost-effective choice for smaller operations, but DDR5 provides the scalability needed for growing businesses.
🏢 Tip: Enterprises planning to expand their infrastructure should invest in DDR5 for long-term scalability and reliability.
For Average Users: Cost-Effectiveness and Practicality
Average users often prioritize affordability and practicality when choosing RAM. For tasks like web browsing, streaming, and office work, DDR4 RAM provides more than enough performance. Its widespread availability and lower cost make it an excellent choice for budget-conscious individuals. Many older systems support DDR4, eliminating the need for expensive upgrades.
DDR5 RAM, on the other hand, offers advanced features and higher speeds. However, these benefits may not translate into noticeable improvements for everyday tasks. For instance, opening multiple browser tabs or running basic productivity software does not fully utilize DDR5’s increased bandwidth. The higher price of DDR5 modules and the need for compatible motherboards make it less practical for average users.
💡 Tip: Users with older systems should consider DDR4 for its cost-effectiveness. Those building new systems might opt for DDR5 to future-proof their setup, but only if the budget allows.
A comparison of DDR4 and DDR5 for average users highlights their practicality:
|
Feature |
DDR4 |
DDR5 |
|---|---|---|
|
Cost |
Affordable |
Higher |
|
Compatibility |
Works with older systems |
Requires newer hardware |
|
Performance for Basics |
More than sufficient |
Overkill for most tasks |
|
Future-Proofing |
Limited |
Better for long-term use |
For average users, DDR4 and DDR5 memory (RAM) parts commonly used in desktops serve different purposes. DDR4 remains the go-to option for those seeking value and compatibility. DDR5 suits users planning for future upgrades but may not justify the cost for basic needs.
Is It Worth Upgrading to DDR5 RAM?
Factors to Consider Before Upgrading
Upgrading to DDR5 RAM depends on several factors, including system requirements, workload demands, and compatibility. DDR5 offers significant improvements in speed, bandwidth, and density compared to DDR4. For users running memory-intensive applications like AI, machine learning, or big data analytics, DDR5 provides the necessary performance boost. Its ability to handle larger datasets efficiently makes it ideal for enterprise servers and high-performance desktops.
Compatibility remains a critical consideration. DDR5 requires motherboards and CPUs designed for its architecture. Users upgrading older systems may face challenges due to the lack of backward compatibility. Additionally, DDR5 modules integrate advanced features like Power Management Integrated Circuits (PMIC) and built-in error correction (ECC), which enhance reliability but demand updated hardware.
Recent benchmarks highlight DDR5’s advantages. DDR5-5600 CL46 achieves a system bandwidth of 69.2 GB/s, compared to DDR4-3200 CL22 at 33.6 GB/s. Gaming applications show up to 23% higher FPS at 1080p, while content creation tools like DaVinci Resolve demonstrate nearly 11% faster performance. These improvements make DDR5 a compelling choice for users seeking enhanced performance in demanding scenarios.
💡 Tip: Evaluate your system’s compatibility and workload requirements before upgrading to DDR5. Users with older systems may find DDR4 sufficient for their needs.
Budget vs. Performance Gains
The decision to upgrade to DDR5 RAM often hinges on balancing cost and performance. DDR5 modules are more expensive than DDR4, reflecting their advanced features and higher speeds. However, the performance gains justify the investment for users with demanding workloads. For instance, DDR5 delivers up to 21% improvement in video transcoding tasks and noticeable gains in gaming and production workloads.
Budget constraints play a significant role in determining the feasibility of upgrading. Users with limited budgets may prioritize DDR4 for its affordability and compatibility with older systems. DDR4 remains a cost-effective option for everyday tasks like web browsing and office work. On the other hand, professionals and gamers building new systems may opt for DDR5 to future-proof their setups.
|
Aspect |
DDR4 Performance |
DDR5 Performance |
|---|---|---|
|
Gaming Performance |
Minimal gains, < 3% improvement |
Slightly better in some scenarios |
|
Production Workloads |
Slight advantage in gear 1 mode |
Up to 21% improvement in video transcoding |
|
Cost Implications |
More affordable |
Higher costs for current options |
🧠 Note: Consider your budget and workload demands carefully. DDR5 offers long-term benefits but may not justify the cost for basic tasks.
Future-Proofing Your System
DDR5 RAM represents the future of memory technology, offering scalability and reliability for evolving computing environments. Its ability to support larger capacities, up to 128 GB per stick, makes it essential for modern applications like cloud computing and big data analytics. DDR5’s reduced power consumption and built-in ECC capabilities enhance efficiency and data integrity, making it ideal for enterprise servers and mobile devices.
The transition to DDR5 aligns with the increasing demands of AI, machine learning, and virtualization. As software and hardware continue to evolve, DDR5 ensures compatibility with next-gen platforms. Its higher bandwidth and density provide the foundation for handling complex workloads and larger datasets.
|
Aspect |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Scalability |
DDR5 supports larger capacities, up to 128 GB per stick, essential for modern applications like cloud computing and big data analytics. |
|
Capacity |
DDR5 modules can support up to 64GB per stick, significantly surpassing DDR4’s 16GB limit, enhancing performance in data-intensive tasks. |
|
Power Efficiency |
Operating at 1.1V, DDR5 reduces power consumption and heat generation, crucial for mobile devices and data centers. |
|
Reliability |
Built-in ECC capabilities enhance data integrity, making DDR5 ideal for enterprise applications. |
|
Evolutionary Necessity |
Transitioning to DDR5 is essential due to the increasing demands of modern computing environments, driven by cloud computing and AI. |
🔋 Tip: Users planning to upgrade their systems for long-term scalability should consider DDR5. Its advanced features ensure compatibility with future technologies.
Choosing between DDR4 and DDR5 RAM depends on performance needs, compatibility, and budget. DDR5 offers advancements like higher transfer rates, dual-channel architecture, and on-die ECC, making it ideal for high-performance tasks. DDR4 remains a cost-effective option for everyday use and older systems.
|
Parameter |
DDR4 SDRAM |
DDR5 SDRAM |
|---|---|---|
|
Release Date |
Q2 2014 |
2020 |
|
Operating Voltage |
1.2V |
1.1V |
|
Transfer Rate |
1600–5000 MT/s |
Up to 8400 MT/s |
|
Max DIMM Capacity |
64 GB |
128 GB |
|
Architecture |
Single Channel |
Dual Independent Channels |
|
ECC Support |
Optional Module |
On-die ECC and optional ECC modules |
|
Power Management |
Motherboard-based |
Integrated Voltage Regulator |
💡 Tip: Gamers and professionals should consider DDR5 for future-proofing, while DDR4 suits users prioritizing affordability and compatibility. Balancing performance with cost ensures the best value for your system.
What is the main difference between DDR4 and DDR5 RAM?
DDR5 RAM offers higher speeds, increased bandwidth, and larger capacities compared to DDR4. It also includes advanced features like on-die ECC and integrated power management. DDR4, however, remains more affordable and compatible with older systems, making it a practical choice for many users.
💡 Tip: Choose DDR5 for future-proofing and high-performance tasks, while DDR4 suits budget-conscious users.
Can DDR4 and DDR5 RAM be used together in the same system?
No, DDR4 and DDR5 RAM cannot be used together. They have different architectures and physical designs. Each requires a motherboard specifically designed for its type, with unique DIMM slot configurations that prevent cross-compatibility.
🧠 Note: Always check your motherboard’s specifications before purchasing RAM.
Is DDR5 RAM worth the higher cost?
DDR5 RAM justifies its cost for users needing high performance, such as gamers, content creators, and enterprise professionals. Its advanced features and future-proof capabilities make it ideal for demanding tasks. However, for basic computing needs, DDR4 remains a cost-effective and sufficient option.
How does DDR5 improve energy efficiency?
DDR5 RAM operates at a lower voltage (1.1V) compared to DDR4 (1.2V). It also integrates Power Management Integrated Circuits (PMIC) directly onto the module. These features reduce power consumption and heat generation, making DDR5 more energy-efficient, especially for laptops and servers.
What should average users consider when choosing between DDR4 and DDR5?
Average users should prioritize affordability and compatibility. DDR4 provides sufficient performance for everyday tasks like browsing and office work. DDR5 offers future-proofing but may not deliver noticeable benefits for basic use. Budget and system compatibility should guide the decision.
💡 Tip: For older systems, DDR4 is the practical choice. For new builds, consider DDR5 if the budget allows.
See Also
Integrating AEAT-8800-Q24 to Boost Robotics Efficiency
Understanding MC9S12DJ256MFUE Specs for Automotive Use
Key Specifications of MC9S12XEQ512CAL You Should Know
RV1126: Driving AI Edge Computing in Robotics
Three Essential Features of SPC5605BMLL6 and SPC5607BMLL6 ECUs