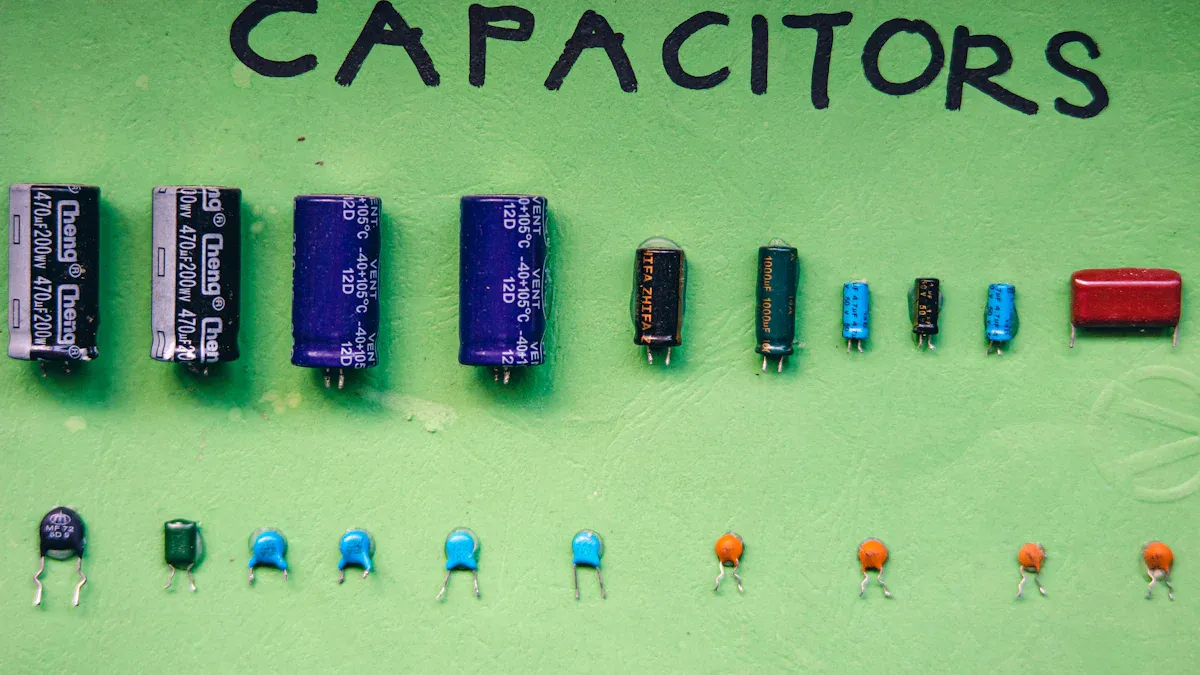
Capacitors are crucial components in electronics, essential for power conditioning in various devices like audio amplifiers and DC-DC converters. Engineers frequently face the decision of choosing between an electrolytic capacitor vs ceramic capacitor. Electrolytic capacitors are known for their high capacitance, making them excellent for power filtering applications. In contrast, ceramic capacitors excel in high-frequency circuits due to their stability and compact size. This article will delve into the specific characteristics of each type to guide you on when to select an electrolytic capacitor versus a ceramic capacitor.
Key Takeaways
-
Electrolytic capacitors hold much power. They make power smooth in devices. They are larger in size.
-
Ceramic capacitors are tiny. They work well in quick circuits. They block unwanted noise. They are very steady.
-
Electrolytic capacitors need a certain connection. Ceramic capacitors can connect any way.
-
Engineers often use both kinds. Electrolytic capacitors fix slow noise. Ceramic capacitors fix fast noise.
-
Pick the best capacitor. Think about your circuit’s needs. Consider power amount and speed.
Understanding Capacitor Fundamentals
Capacitors are basic electronic parts. They hold electrical energy. This energy is in an electric field. Knowing how they are built helps. It shows why they act differently.
Electrolytic Capacitors: Construction and Polarity
Electrolytic capacitors have a special build. They use a liquid or gel. This is a conductive plate. Aluminum foil is the anode. This is the positive end. A very thin oxide layer grows. It is on this foil. This layer is the dielectric. Another foil or the liquid is the cathode. This is the negative end. This design gives high capacitance. They can store much charge. Electrolytic capacitors have polarity. They must connect a certain way. The positive end needs higher voltage. The negative end needs lower voltage. Wrong connection is bad. It can make them overheat. They can swell or burst. Engineers must check polarity. Do this when installing them.
Ceramic Capacitors: Construction and Non-Polarity
Ceramic capacitors are built differently. They use a ceramic material. This is their dielectric. This ceramic is an insulator. Metal layers are on both sides. They act as electrodes. Many are MLCCs. These have many layers. They alternate ceramic and metal. This stacked build makes them small. They still have good capacitance. It also makes them reliable. A big plus is non-polarity. They have no positive or negative end. Engineers can put them in any way. No damage will happen. This makes circuits easier. It simplifies putting them together. Their non-polarized nature is useful.
Electrolytic vs Ceramic Capacitor: Key Performance Differences
Engineers look at many things. They compare electrolytic and ceramic capacitors. This helps them pick the right part. Ceramic capacitors work faster. They have less internal resistance. They also leak less electricity. This is compared to electrolytic types.
Capacitance Range and Physical Size
Capacitance is a big difference. Electrolytic capacitors store more charge. This is compared to ceramic ones. They usually range from 47µF to 1000µF. They are good for storing a lot of power. But they are also bigger. This is for the same amount of charge.
Ceramic capacitors store less charge. A common one is 0.1µF. They are known to be small. Their design makes them tiny. This is good for small devices.
ESR, ESL, and Frequency Response
ESR and ESL affect how capacitors work. ESR is the capacitor’s inner resistance. ESL is its inner inductance. Both make capacitors less effective. This is true at high frequencies.
Ceramic capacitors have low ESR and ESL. They react very fast. They handle voltage changes quickly. This makes them great for high frequencies. They can block high-frequency noise well.
Electrolytic capacitors have higher ESR. For example, some have 3 to 15 mΩ. Others can be as low as 3 mΩ. Some go down to 5 mΩ. Other types also have low ESR. But we don’t know how ESR changes. This is at different frequencies.
Electrolytic capacitors also have higher ESL. ESL is the wire’s inductance. It resists changes in AC current. High ESL and ESR make them bad at high frequencies. Their performance gets worse. This happens with high heat and frequencies. This means high frequencies hurt them.
Voltage Rating and Ripple Current
Voltage rating is the max voltage. A capacitor can handle it safely. Too much voltage can break it.
Electrolytic capacitors have many voltage ratings. Common ones are 16V, 25V, and 50V. Some go from 25V to 80V. They often handle higher voltages. This is for certain uses. They also handle more ripple current. Ripple current is AC in DC voltage. Electrolytic capacitors are bigger. This helps them cool down. So they can handle more ripple current.
Ceramic capacitors also have many voltage ratings. They can be 2.5V, 25V, 100V, 630V, 1kV, and 1250V. Some range from 50V to 1000V. They can handle high voltage. But they handle less ripple current. This is compared to electrolytic ones.
Temperature Stability and Leakage Current
Temperature stability means steady performance. This is at different temperatures. Leakage current is a small current. It flows when voltage is on.
Ceramic capacitors work well in heat. Their charge stays the same. This is over many temperatures. They also have very low leakage. This makes them good for exact circuits.
Electrolytic capacitors change more with heat. Their charge and ESR can vary a lot. They also leak more current. This means they slowly lose charge. This happens even when not in use. This can be a problem. This is for battery-powered devices.
Polarity and Cost
Polarity is a key difference. Electrolytic capacitors have polarity. They must connect correctly. Positive to positive, negative to negative. Wrong connection can cause damage. It can even cause an explosion. This makes circuit design harder.
Ceramic capacitors have no polarity. Engineers can put them in any way. This makes circuit design easier. It also makes building easier.
Cost is another factor. For very high charge, electrolytic are cheaper. But for small charge, ceramic are cheaper. This is especially for small parts. Ceramic capacitor costs have dropped. This makes them a popular choice.
Optimal Applications for Each Capacitor
Picking the right capacitor is key. It depends on circuit needs. Each type works best in certain areas. Knowing these helps engineers choose. The choice is often between an electrolytic capacitor vs ceramic capacitor.
Electrolytic Capacitor Applications
Electrolytic capacitors are great for high capacitance. They handle big power well. They also work with low-frequency signals.
-
Power Supply Filtering and Smoothing: They are key in power supplies. They smooth voltage changes. Their high capacitance helps. They filter out ripple voltage. This makes power stable.
-
Audio Coupling and Blocking: These are in audio circuits. They link signals between parts. They also block unwanted DC.
-
Audio amplifiers use them. This includes phones.
-
They link and unlink signals. This is in many circuits.
-
Makers sell aluminum electrolytic capacitors. They are for ‘Sound Equipment’.
-
-
Motor Starting and Running Circuits: Big electrolytic capacitors give motors a start. They give a quick burst of power. They also help motors run steady.
-
Energy Storage: Circuits needing quick power use them. They store energy. They release it fast.
-
LED Drivers: They smooth current to LEDs. This stops flickering. It makes light steady.
-
Amplifiers: They stabilize power. They filter noise. This is in many amplifiers.
-
Audio Crossover Networks: In speakers, they split sounds. They send high, mid, low sounds. Each goes to the right speaker.
-
Timing Circuits: They give needed capacitance. This is for long time delays.
Ceramic Capacitor Applications
Ceramic capacitors are great for high frequencies. They are stable and small. They have low unwanted effects.
-
Radio Communications: They work well at high frequencies. This makes them good for radios. They handle fast signals.
-
Data Transfer: They keep data signals clear. This is in fast data lines. They stop data errors.
-
Noise Filtering: They filter out high-frequency noise. This keeps signals clean. This is for sensitive circuits.
-
High-Frequency Decoupling: They are key for power lines. They stop noise from spreading.
-
MLCCs are used a lot. This is in new electronics.
-
They work great at different frequencies. This is because they have low resistance. They also have low inductance.
-
MLCCs are used most. They are for DC-DC converter filters.
-
They are cheap. They have low ESR. They have low ESL. This makes them a top choice.
-
-
Avionics Systems: They are reliable and small. This is vital in airplane electronics.
-
Communication Equipment: They are needed in cell phones. They are also in Wi-Fi routers. They handle high frequencies. They filter noise.
-
Power Supply in Aerospace: They work well in tough places. This makes them good for aerospace power.
-
High-Density PCBs: They are tiny. This allows small designs. This is key for small electronics.
-
Oscillation, Timing, Clock, and Delay Circuits: They are precise and stable. This makes them good for timing signals.
-
Bypass Filtering: They are near chips. They send high-frequency noise to ground.
Choosing the Right Capacitor: A Decision Guide
Engineers choose between an electrolytic capacitor vs ceramic capacitor. They need to pick the best one. This depends on what the circuit needs. Each type has good points.
Key Selection Factors
Many things help choose a capacitor. Engineers think about these.
-
Frequency Response: Use ceramic capacitors for fast signals. They work well with high frequencies. Electrolytic capacitors are better for slow signals.
-
Capacitance Value: Circuits needing much charge use electrolytic capacitors. They store more power. Ceramic capacitors are for less charge.
-
Physical Size: New electronics are small. Ceramic capacitors are tiny. They fit in small spaces. Electrolytic capacitors are bigger. This is for the same charge.
-
Voltage Rating: The capacitor must handle the circuit’s power. Both types have different ratings. Engineers pick one stronger than needed.
-
Temperature Stability: Ceramic capacitors work well in all temperatures. Electrolytic capacitors change more with heat.
-
Cost: For much charge, electrolytic capacitors cost less. For little charge, ceramic capacitors are cheaper.
Combining Capacitor Types
Many circuits use both types. This makes the most of each one.
-
Engineers often mix electrolytic and ceramic capacitors. Electrolytic capacitors clean up slow noise. This is usually 1KHz or less.
-
Ceramic capacitors clean up fast noise. They work well with electrolytic capacitors. This is for high-frequency uses.
-
In power supplies, electrolytic capacitors remove AC ripple. They smooth signals. They act like filters. They let DC signals pass.
-
MLCCs are common in DC-DC converters. They help electrolytic capacitors. They handle fast noise. This mix makes strong filters.
No single “best” capacitor exists. The best choice depends on the use. Electrolytic capacitors store much charge. They are great for power filtering. They smooth DC signals. They are key for power needs. They work for low-frequency tasks. Supercapacitors are electrolytic types. They store huge amounts of power. Ceramic capacitors are good for high frequencies. They are stable and small. They work well for exact tasks. Engineers must know circuit needs. Think about frequency and voltage. Consider current, size, and heat. Also, think about cost. This helps them choose wisely. Both types are strong in different ways. Engineers should use these strengths. This makes designs strong and good.
FAQ
What is the main difference between electrolytic and ceramic capacitors?
Electrolytic capacitors hold much power. They clean up electricity. They are bigger. Ceramic capacitors are steady. They are small. They work well in fast circuits. They are tiny.
When should engineers choose an electrolytic capacitor?
Engineers pick electrolytic capacitors. They need to store a lot of power. They are good for power supplies. They make power smooth. They store energy. They also work for slow signals.
When should engineers choose a ceramic capacitor?
Engineers pick ceramic capacitors. They are for fast circuits. They are steady. They are small. They have low ESR. They are good for blocking noise. They fit in small spots.
Can engineers use both capacitor types in one circuit?
Yes, engineers often mix them. Electrolytic capacitors stop slow noise. Ceramic capacitors stop fast noise. This makes strong filters.
What happens if someone connects an electrolytic capacitor incorrectly?
Wrong connection causes issues. It can get too hot. It might swell. It could even burst. This is because of its polarity. Always link the plus side to more voltage.
See Also
Coilcraft XPL2010: High-Performance Inductors for Optimal VRM/VRD Design Analysis
STM32F401VCT6 vs STR750FV2T6: Core MCU Selection for Medical Equipment
SPC5605BMLL6 and SPC5607BMLL6 ECUs: Automotive Technology and Future Applications Explored
Electronic Components: Innovation, Quality, and Future Trends for Industry Excellence

