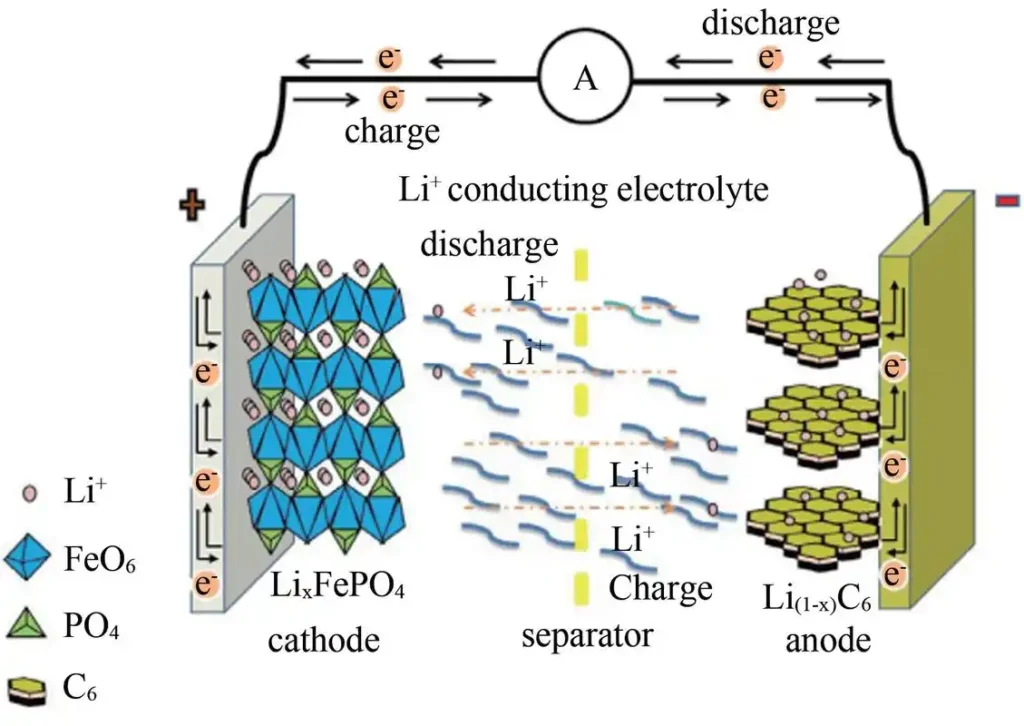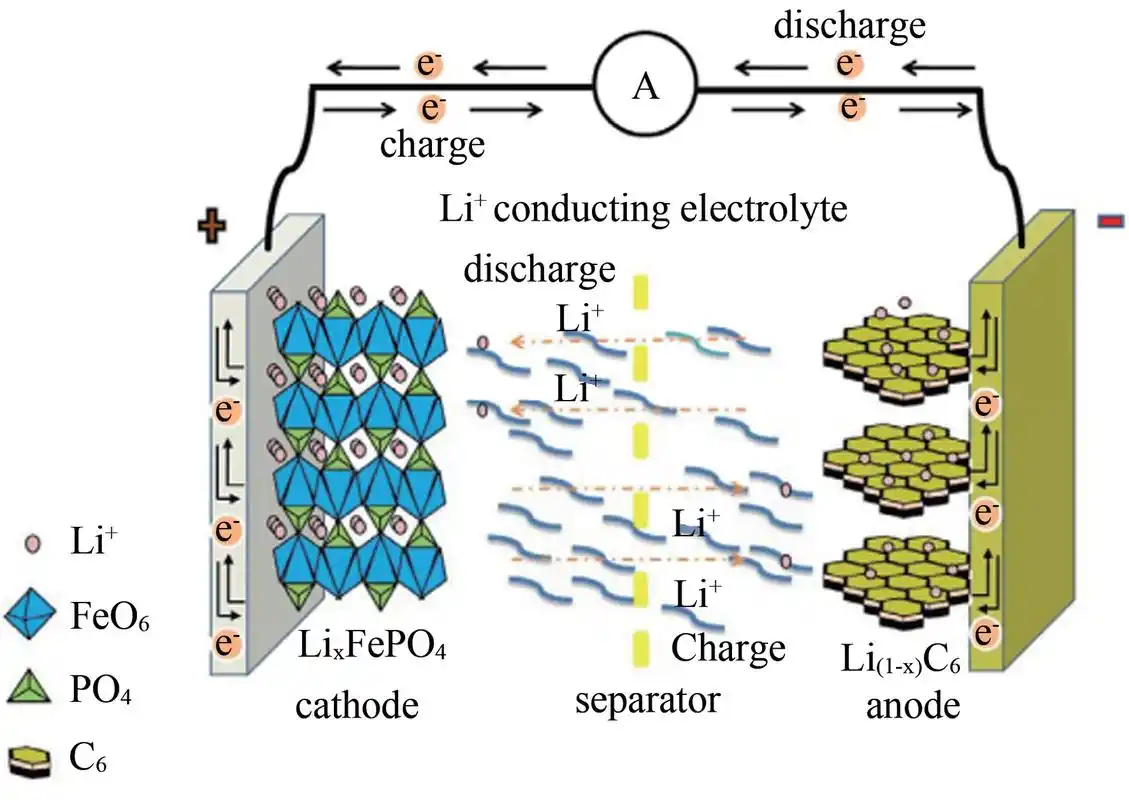
The global battery market plays a crucial role in advancing modern technology and supporting clean energy initiatives. Its rapid expansion highlights the increasing demand for sustainable energy solutions.
-
The lithium-ion batteries market is projected to reach USD 257 billion by 2030, while lead-acid batteries could grow to USD 121 billion during the same period.
-
Batteries, including lithium-ion batteries, for electric vehicles and energy storage systems are currently valued at USD 120 billion. These markets are expected to surge to USD 500 billion by 2030 under a Net Zero Emissions strategy.
-
The global battery market is anticipated to grow from USD 95.7 billion in 2022 to USD 136.6 billion by 2027, reflecting an annual growth rate of 7.4%.
Exports play a pivotal role in driving innovation and growth within the battery industry. Between 2015 and 2022, Europe exported more batteries than it imported, underscoring how battery trade fosters advancements in production and technology.
Lithium-ion batteries, lead-acid batteries, and sodium-based batteries are essential for global economic and technological progress, shaping the future of energy solutions worldwide.
Key Takeaways
-
The world battery market is growing fast, reaching $329.8 billion by 2030. This growth is due to electric cars and clean energy.
-
Lithium-ion batteries are key for electric cars and storing energy. They last long and store a lot of power, making them popular in many fields.
-
Sodium-ion batteries are cheaper and safer than lithium-ion ones. They could be widely used for energy storage and electric cars.
-
Recycling and eco-friendly methods are important for making batteries. These help lower harm to nature and use fewer raw materials.
-
Trade rules and new ideas are changing the battery market. Countries aim to be self-sufficient and eco-friendly to protect their supplies.
Global Battery Market Overview
Market size and growth projections
The battery market is growing fast due to energy storage needs. In 2023, it was worth USD 118.2 billion. By 2030, it may grow to USD 329.8 billion, with a yearly growth rate of 15.8%.
This growth is due to more electric cars, renewable energy, and better gadgets. Batteries are getting cheaper, with costs per kWh dropping to $32–$54 by 2030.
Key drivers: EVs, renewable energy, and consumer electronics
Electric cars are a big reason for battery demand. EV sales hit 13.7 million, with Europe seeing 17% growth from 2022 to 2023. The EV market is now worth USD 769.4 billion. Lithium-ion batteries, known for being powerful and efficient, are key for EVs.
Renewable energy also boosts battery use. Batteries store energy from solar and wind power, keeping energy steady. Gadgets like phones and laptops also need small, reliable batteries.
Regional leaders and production hubs
North America leads the battery market with advanced tech and research. It has a strong supply chain and helpful rules. Asia-Pacific, including China, India, and South Korea, is growing fast. Government support and more EVs help production there.
Europe is also important, focusing on green energy and new ideas. These regions together grow the battery market and improve technology.
Lithium-Ion Batteries

Why Lithium-Ion Batteries Are Popular
Lithium-ion batteries are very important in the global market. They have high energy density (200-300 Wh/kg) and last long (500-2000 cycles). These features make them useful in many industries.
They are used in different areas:
-
Power Batteries: Electric cars need lithium-ion batteries to run. Companies like Tesla and BYD use them. BYD’s blade battery is getting noticed. Electric scooters, like Yadea’s, are switching from lead-acid to lithium-ion batteries.
-
Consumer Electronics: Phones, laptops, and headphones use these batteries. For example, Apple iPhones and Huawei laptops rely on them because they are small and efficient.
-
Energy Storage Systems: These batteries store energy for later use. Big systems in California and home setups like Tesla Powerwall use them to save renewable energy.
The table below shows where lithium-ion batteries are used and their market share:
|
Application Segment |
Market Share (%) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Consumer Electronics |
>31.0 |
Biggest revenue share in 2023, includes phones, laptops, and portable devices. |
|
Automotive |
Fastest-growing |
Growth due to electric and hybrid cars, driven by fuel costs and environment concerns. |
|
Energy Storage Systems |
N/A |
Used for backup power in homes and buildings with solar panels. |
|
Industrial Applications |
N/A |
Includes tools, boats, and machines in different industries. |
|
Regional Market (Asia Pacific) |
>47.0 |
Largest market share, growing fast in electric cars and energy storage. |
Export Growth and Top Exporters
China’s lithium-ion battery exports have grown a lot. From 2017 to 2022, exports grew 20%-35% each year. In 2021, exports were worth CNY 183.526 billion, up 66.5% from 2020. By 2022, exports reached CNY 342.656 billion, an 86.7% increase.
Key export facts:
-
The U.S., Germany, and South Korea buy the most from China. In 2022, the U.S. bought $3.934 billion, Germany $3.382 billion, and South Korea $1.175 billion.
-
Exports to the U.S. grew by 65.66% in one year, showing high demand.
-
Early 2023 data shows exports are still strong, thanks to electric cars and energy storage systems.
China leads in exports because of its advanced factories and big investments in research. In 2023, China’s exports were over $65 billion, making up 65% of the global market.
Problems: Materials and Recycling
Lithium-ion batteries have some problems with materials and recycling. Battery chemistry keeps changing, so recycling methods must improve. New rules in China and Europe aim to help recycling, but their effects are unclear.
Main problems include:
-
Old batteries are hard to recycle for new materials.
-
New recycling methods use less energy and lower costs. They also cut carbon emissions by about 25%.
-
Recycling must be cost-effective to solve these issues.
Better recycling and less reliance on raw materials are key for the future of lithium-ion batteries.
Lead-Acid Batteries
Common uses and importance
Lead-acid batteries are still very important worldwide. They are cheap and work well, even with newer options like lithium-ion batteries. These batteries are used in many areas:
-
Automotive Sector: Cars use these batteries for starting and lighting. More cars in growing countries keep demand high.
-
Industrial Applications: They are strong and great for backup power in telecom and data centers. This helps keep systems running.
-
Commercial Use: Emergency lights, fire alarms, and security systems depend on them. They are useful as energy-saving becomes more important.
-
Residential Sector: In places with weak electricity grids, they give backup power. They also help with renewable energy systems.
These batteries are useful and affordable, so they stay important even as new technologies grow.
Exports and competition
Lead-acid battery exports face tough competition. Asia Pacific leads because of high demand in cars and power utilities. In 2020, China had 56% of the market, showing its strength in electric and hybrid car sales.
|
Region |
Market Features |
|---|---|
|
United States |
Many makers, causing a spread-out market. |
|
China |
Big market share and top in electric car sales. |
|
Japan |
Actively involved in the lead-acid battery market. |
Tariffs have changed the U.S. market. Local makers get price benefits, but they must improve and innovate. China stays strong in making and exporting, keeping its top spot globally.
Environmental issues and recycling
Lead-acid batteries can harm the environment. They have lead and acid, which can pollute soil and water if not handled right. But they are highly recyclable. Up to 99% of the lead can be reused, making them one of the most recycled products.
Efforts are ongoing to make recycling better and safer. Many countries now have stricter rules for handling and disposal. The challenge is to balance environmental safety with the need for cheap energy storage.
Solar Cells in Renewable Energy

Role in energy storage and adoption
Solar cells turn sunlight into electricity for clean energy. When paired with batteries, they store power for later use. This setup lets solar energy work at night or on cloudy days.
Solar panels with batteries make the power grid stronger. Batteries help balance energy use by saving power during the day and using it at night. This setup reduces energy demand spikes and keeps the grid steady.
Solar cells are popular because they help reduce fossil fuel use. Homes, businesses, and factories use them to support clean energy goals.
Export opportunities and market leaders
Solar cells are in high demand worldwide, especially in Asia-Pacific. Countries there have rules and programs to promote solar energy. These include tax breaks, financial help, and special rates for selling solar power.
-
Asia-Pacific leads the solar cell market, creating export chances.
-
Governments offer support to grow solar energy use.
-
Programs like Feed-in tariffs and tax cuts help new solar technologies.
China, India, and South Korea are top producers of solar cells. Their advanced factories and helpful policies make them global leaders.
Challenges: costs and supply chain
Solar cells face problems with costs and supply chains. Making them in the U.S. costs more than in China due to higher labor expenses.
-
U.S. labor costs are 22% of production costs, while China’s are 8%.
-
Importing materials adds 11% to U.S. costs, making production pricier.
-
China has cheaper labor, giving it a cost advantage.
Supply chain issues also include ethical concerns. Checking fair labor practices and supplier honesty is hard in some areas. Fixing these problems needs money and better policies to grow the solar cell industry responsibly.
Sodium-Ion Batteries
Benefits and New Uses
Sodium-ion batteries have many benefits for different uses. They are safer and cheaper than lithium-ion batteries. This makes them great for small, affordable electric cars. They give steady power, which is useful for data centers and big energy storage systems. They also lower the risk of overheating, which is helpful in crowded areas.
Main benefits include:
-
A supply chain less affected by global politics.
-
Easy to make using current lithium-ion battery factories.
-
Can take a big part of the energy storage market for homes and vehicles.
These features make sodium-ion batteries a strong choice for future energy needs.
Improvements in Technology
New sodium-ion battery designs focus on better performance and easier production. Companies like Hithium and CATL have made batteries that last longer and work well. For example, Hithium’s Cell N162Ah keeps 94.2% of its power after 4,000 uses. CATL’s second-generation battery works even in very cold weather, down to -40°C.
|
Date |
Company |
Product/Technology Description |
Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Dec 2024 |
Hithium |
First sodium-ion battery for energy storage, Cell N162Ah |
Keeps 94.2% power after 4,000 uses, lasts over 20,000 cycles at 70% health. |
|
Nov 2024 |
CATL |
Second-generation sodium-ion battery |
Works well at -40°C, ready for sale in 2025. |
|
June 2024 |
HiNa Battery |
World’s first 100MWh sodium-ion energy storage project |
Uses 185Ah cells, charges fast, works in different temperatures. |
Sodium-ion batteries work like lithium-ion ones but use sodium instead of lithium. Their parts, like Prussian blue analogs, are cheaper and better for the environment. These updates aim to make sodium-ion batteries compete well in the energy market.
Export Growth and Future Plans
The sodium-ion battery market is growing fast because of smart energy storage needs. Economic recovery after COVID-19 has helped this growth. More people in developing countries can now afford these batteries.
Important export factors include:
-
The need for cheaper energy solutions in poorer areas.
-
Trade and pricing that show sodium-ion batteries are competitive globally.
-
Meeting the demand for advanced energy storage systems.
Sodium-ion batteries could become key in energy storage soon. They are affordable and easy to scale for both rich and poor countries. By 2025, better energy density and lower costs may make them strong rivals to lithium iron phosphate batteries, boosting exports further.
Global Market Dynamics
Supply chain and critical mineral dependencies
The global battery market relies on key minerals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. These materials are vital for making batteries, but their supply chains face big challenges.
-
Lithium: Australia produces the most lithium, but Chinese companies control much of the market. This creates worries about supply due to political issues.
-
Cobalt: The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) makes 68% of the world’s cobalt but refines almost none. China handles 64% of cobalt refining, which adds risks to the supply chain.
-
Recycling: Recycling can help with mineral shortages. Metals like lithium and cobalt can be reused. However, recycling rates are low because waste management rules differ across countries.
Critical minerals face threats from political tensions, fast-growing demand, and trade problems. These issues disrupt battery production, causing price changes and higher costs.
To fix these problems, countries are finding new sources and improving recycling. But these solutions need a lot of money and teamwork between nations.
Regional trade policies and production hubs
Trade rules and production centers affect the global battery market. Countries are taking steps to grow their industries and reduce risks.
-
United States: Tariffs on Chinese goods have raised costs and changed supply chains.
-
Japan: Plans to make 600 GWh of batteries by 2030 focus on local production.
-
South Korea: Policies aim to take 40% of the global battery market by 2030.
-
European Union: Building gigafactories to make batteries locally and lower import reliance.
-
United Kingdom: Over $2.5 billion invested to improve battery-making abilities.
|
Scenario |
Description |
|---|---|
|
US and EU policies to reduce risks |
Strong rules aim to make supply chains safer and less dependent on imports. |
|
China’s cost advantage vs. new hubs |
China is cheaper, but other regions are growing as alternatives. |
These actions show how countries are focusing on self-reliance and sustainability to secure their battery supply chains.
Innovations and sustainability efforts
New ideas and eco-friendly efforts are changing the battery market. Companies and governments are working to make batteries better, greener, and more transparent.
-
Battery Passports: A digital record tracks a battery’s lifecycle. It shows its environmental and social impacts to encourage sustainable practices.
-
Sustainability Audits: CATL created the CREDIT tool to check sustainability in the lithium-ion battery supply chain. This promotes responsible sourcing.
-
EU Mandates: By 2027, the EU will require battery passports to ensure accountability in production.
Innovation is key to making batteries more sustainable. Better technology and new materials improve performance while reducing harm to the environment.
New business ideas also reflect this change. About 64% of mobility companies are testing battery swapping. Many car companies are looking into battery leasing and Battery-as-a-Service (BaaS). These models save energy and cut waste.
|
Trend |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Managing Risks |
Finding weak points to prevent problems early. |
|
Sustainability |
Using eco-friendly methods to improve operations. |
|
Predicting Customer Needs |
Using smart tools to guess demand in changing markets. |
The battery market is growing fast. New ideas and eco-friendly efforts are shaping a cleaner and smarter future.
The global battery market is changing fast. This is due to better technology and the need for clean energy. Important trends include more electric cars, storing renewable energy, and new batteries like sodium-ion. These changes show how important batteries are for the future of energy.
Exports help the battery industry grow and improve.
-
Trading batteries spreads new ideas and grows global markets.
-
Competing worldwide pushes companies to create better products.
-
Tools like the internet make it easier to sell batteries globally.
The future of batteries depends on being eco-friendly and efficient. Countries are working on recycling and using new materials. This will grow global trade and bring nations together. 🌍
What makes the global battery market grow?
The battery market grows because of electric cars, renewable energy, and gadgets. These need better, cheaper, and greener energy options, driving progress.
Why are lithium-ion batteries so popular?
Lithium-ion batteries are light, last long, and store lots of energy. This makes them great for electric cars, small devices, and saving energy.
How are sodium-ion batteries different from lithium-ion ones?
Sodium-ion batteries cost less and are safer to use. They use common materials like sodium but store less energy, so they have fewer uses.
What problems happen with battery recycling?
Recycling batteries is costly and uses a lot of energy. Rules differ by country, making it hard to reuse materials like lithium and cobalt.
Which countries are top in making and selling batteries?
China leads in making and selling batteries with strong factories and support. The U.S., South Korea, and Japan also focus on new ideas and local production.
See Also
Ensuring Quality in Electronics Through Advancing Technologies
Improving Smartphone Screens with MAX8647ETE+T Technology
Understanding MC9S12DJ256MFUE Features for Automotive Uses
Unveiling LPQ252-CEF for Superior Power Efficiency
Three Key Benefits of XCF01SVOG20C in Automation