
The market offers an overwhelming variety of SMD LED chips, making selection a challenge for any lighting project. A carefully chosen chip ensures project success, optimal performance, and long-term durability in all lighting applications. This guide empowers readers to make informed decisions for their specific strip lighting needs in 2026. It highlights the importance of understanding key specifications beyond just brightness for effective LED chip lighting. Proper selection impacts the overall quality of any LED light, including strip lighting and other LED lighting solutions. Choosing the correct SMD chip is vital for any LED lighting design, ensuring optimal light output from every LED.
Key Takeaways
-
Understand SMD LED chip names. Numbers like ‘3528’ show the chip’s size in millimeters.
-
Match the LED chip to your project needs. Consider brightness, power, and where you will use it.
-
Check key performance numbers. Look at how much light it makes, its color, and how well it shows colors.
-
Ensure quality and long life. Good chips last longer and need proper cooling. Choose trusted brands.
-
Plan how to use the chip. Pick the right power supply and install it correctly for the best results.
Understanding SMD LED Basics

What are SMD LEDs
Surface-Mount Device (SMD) LEDs represent a significant advancement in LED technology. These small, flat chips mount directly onto a circuit board. This design allows for compact and versatile lighting solutions. SMD LEDs are widely used in various applications, from general lighting to intricate display systems. They offer excellent light output and reliability, making them a popular choice for modern lighting projects. Each SMD LED chip provides consistent and efficient light.
Common SMD Chip Types
The market offers many common SMD chip types, each with distinct characteristics. Newer SMD LED chip styles, such as 2835, 3020, and 3014, provide increased efficiency and brightness. These chips are often more efficient than older models. For example, the SMD2835 chip is known for its high efficiency. In contrast, the SMD5050 chip delivers higher brightness but consumes more power and generates more heat, typically around 0.2-0.24W per LED. SMD5050 chips are versatile for various lighting needs. They are suitable for:
-
Mood lighting
-
Embellishing costumes or props with visual effects
-
Constructing interactive installations
-
Refrigerator lamps
-
Night lights
These common led chip types offer different performance levels for strip lighting and other LED applications. Selecting the right chip depends on the specific lighting requirements.
Deciphering Chip Naming
Manufacturers use a numbering system to indicate the physical dimensions of SMD chips. This system helps users identify the size of each led chip. For instance, the number “3528” means the chip measures 3.5mm by 2.8mm. Similarly, “5050” indicates a chip that is 5.0mm by 5.0mm. This naming convention applies across many SMD led chips.
|
SMD LED Chip |
Width (mm) |
Length (mm) |
|---|---|---|
|
3528 |
3.5 |
2.8 |
|
5050 |
5.0 |
5.0 |
|
2835 |
2.8 |
3.5 |
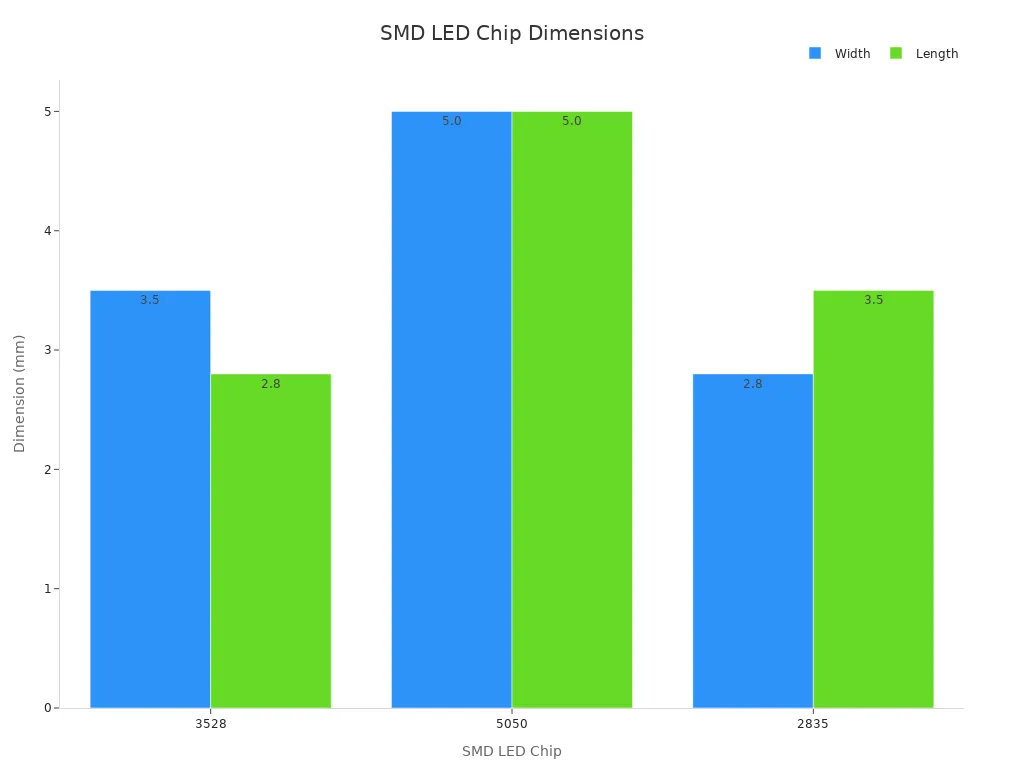
Understanding these numbers helps in selecting the correct SMD for strip lighting or other led chip lighting projects. It ensures compatibility and proper fit for the intended lighting design.
Defining Your Project Needs
Choosing the right SMD LED involves matching application requirements to the appropriate component. SMD LED technology enables smaller pixel pitch for clearer, more vibrant visuals. This makes it ideal for high-definition displays and promotes energy efficiency. For any project, selecting high-quality LED light strips with the correct LED chip type and density is crucial. This ensures optimal performance and longevity for all lighting solutions.
Brightness and Luminous Flux
Brightness and luminous flux are critical factors when selecting an SMD LED chip. Luminous flux, measured in ANSI lumens, provides an objective measure of the total light output from an LED. However, perceived brightness is subjective. It is significantly influenced by color saturation, a phenomenon known as the Helmholtz–Kohlrausch Effect. Highly saturated colors, common in LED and laser light sources, appear brighter than less saturated colors. This happens even when their objective luminance levels are identical. Therefore, LED projectors with wide color gamuts can seem brighter than their ANSI lumen specifications suggest. Ambient light or content with less vibrant colors can reduce this effect. Understanding this distinction helps in selecting the right chip for the desired visual impact. The overall brightness of the light depends on these factors.
Power and Voltage Match
Matching the power and voltage of your SMD LED chip to your power supply is essential. Each LED chip has a specific forward voltage and current requirement. Supplying too much voltage or current can damage the LED, shortening its lifespan. Conversely, insufficient power will result in dim or non-functional lighting. For example, a 12V LED strip light requires a 12V power supply. A 24V LED strip light needs a 24V power supply. Proper voltage matching ensures the LED operates at its optimal efficiency. This prevents overheating and ensures consistent light output. Always check the specifications of the LED chips and the power supply to ensure compatibility. This step is vital for the longevity and performance of any LED lighting system.
Application Environment
The environment where you install the LED chips significantly impacts your selection. Different environments require different levels of protection for the SMD LED chip. For instance, indoor strip lighting in dry areas may only need basic protection. However, outdoor applications demand robust protection against elements like water and dust.
For outdoor applications, an IP65 waterproof rating is recommended for LED strip lighting. This rating signifies robust protection against water and dust. It ensures the LED strip’s functionality and luminosity even in challenging weather conditions.
|
IP Rating |
Suitable Environment |
|---|---|
|
IP20 |
Dry interiors |
|
IP65 |
Wet or submerged conditions (implying outdoor use) |
Choosing the correct IP rating for your LED strip light ensures durability and safety. This is especially important for outdoor LED strip lighting or any application exposed to moisture.
Beam Angle and Light Spread
The beam angle of an LED chip determines how the light spreads from the source. Different applications require different beam angles for optimal illumination. A narrow beam angle focuses light into a concentrated spot. This is useful for accent lighting or task lighting. A wider beam angle spreads light over a larger area. This works well for general room lighting or floodlighting.
-
A well-designed beam angle ensures high lux levels in key areas without sacrificing overall brightness.
-
Optimized light distribution minimizes light waste. It focuses illumination where it is needed.
-
Precision beam focus is crucial for achieving efficient and effective lighting. This meets the demands of various applications.
A light tower with high lumens but poor light distribution can leave critical areas underlit. It wastes light in less important zones. Therefore, consider the desired light spread for your specific application when selecting an SMD LED chip. This ensures your lighting is both effective and energy-efficient lighting.
Key Performance Metrics
Luminous Efficacy and Efficiency
Luminous efficacy measures how well a light source produces visible light. It represents the ratio of luminous flux (lumens) to the electrical power consumed (watts). A higher efficacy means the LED produces more light for less power, increasing its perceived brightness. This makes the LED more efficient. Choosing a high-efficacy SMD chip reduces energy costs for all types of lighting, including strip lighting. It also minimizes heat generation. This is crucial for sustainable lighting solutions and long-term performance of strip lighting. An efficient LED chip converts most electrical energy into light, not heat.
Color Temperature (CCT)
Color Temperature (CCT) describes the color appearance of the light. It is measured in Kelvin (K). Lower Kelvin values, such as 2700K-3000K, produce warm white light. It has a yellowish-reddish hue. This light creates a cozy atmosphere. People often use it for residential lighting or restaurants, and it can enhance the mood of strip lighting. Mid-range values, like 3500K-4500K, produce neutral white light. It appears balanced. Offices and retail spaces often use it. Higher Kelvin values, such as 5000K-6500K, produce cool white or daylight light. This light has a bluish tint. It enhances alertness and visibility. Industrial settings and task lighting benefit from this, including specialized strip lighting applications. Selecting the correct CCT for your SMD chip ensures the desired ambiance and functionality for the LED lighting. Understanding CCT helps in selecting the perfect strip lighting for any space.
Color Rendering Index (CRI)
The Color Rendering Index (CRI) measures how accurately a light source reveals the true colors of objects compared to natural light. It ranges from 0 to 100. A CRI of 100 means the light source renders colors perfectly, like natural daylight. High CRI values (80-90+) are important for applications where color accuracy is critical. Art galleries, retail stores, and photography studios require high CRI lighting. High CRI values ensure the perceived brightness of colors remains true. For high-end architectural strip lighting, a high CRI is often a key requirement. Low CRI values (below 70) can make colors appear dull or distorted. These chips are suitable for general outdoor lighting or areas where color accuracy is not a priority, like decorative strip lighting. Choosing an SMD chip with an appropriate CRI ensures objects appear vibrant and true-to-life under the emitted light.
Forward Voltage and Current
Forward voltage (Vf) and forward current (If) are fundamental electrical characteristics of an LED. In an LED, the forward voltage (Vf) is the voltage drop across the LED when it is conducting current. The forward current (If) is the current flowing through the LED. The power dissipated by the LED (Pd) is the product of its forward voltage and forward current (Pd = Vf * If). This power is primarily converted into light, but a portion is also dissipated as heat. Therefore, controlling the forward current is crucial for managing power dissipation and preventing damage to the LED. Each SMD chip has specific Vf and If ratings. Exceeding these ratings can permanently damage the chip. It also significantly reduces its lifespan. Matching the power supply to these specifications is vital. It ensures stable operation and optimal brightness of the light for your strip lighting project. Incorrect voltage or current can lead to flickering, premature failure, or inconsistent light output from the strip lighting. Always consult the manufacturer’s datasheet for the specific LED chip. This provides the correct operating parameters for your led chip lighting project. Proper selection ensures the longevity and performance of your led chip lighting.
Ensuring Quality and Durability
Lifespan and Degradation
The lifespan of an LED chip is a crucial factor for any lighting project. Manufacturers often rate LED chips for tens of thousands of hours. However, heat significantly impacts this lifespan. High operating temperatures accelerate light degradation, meaning the LED produces less light over time. Proper thermal management helps maintain the initial brightness and extends the useful life of the LED. This is especially important for strip lighting, where many chips operate in close proximity. A well-chosen chip ensures consistent light output for many years.
Thermal Management
Effective thermal management is vital for the longevity and performance of any LED. LEDs generate heat, and this heat must dissipate efficiently. Poor heat dissipation leads to higher junction temperatures within the chip. This reduces the LED’s efficiency and shortens its lifespan. Designers often use heat sinks, thermal pads, and proper circuit board design to manage heat. For high-power lighting applications, robust thermal solutions are essential. This ensures the LED chip operates within its specified temperature limits, maintaining optimal light quality.
Certifications and Standards
Certifications ensure an LED chip meets specific quality and safety standards. These standards vary by region and application. For example, in Europe, specific certifications apply to different types of original equipment manufacturer (OEM) lighting:
|
Certification |
Product Type |
|---|---|
|
ECE R37 |
OEM halogen |
|
ECE R99 |
OEM Xenon |
|
ECE R128 |
OEM LED |
Currently, no specific homologation requirements or legal certifications exist for LED upgrade bulbs used on public roads in the EU. EU member states have not yet adopted the necessary legislation to legalize these bulbs. The regulation for LED upgrade bulbs is not yet defined in Europe. However, these restrictions do not apply to the use of LED upgrade bulbs on private roads. When assessing conformity under the EU General Product Safety Regulation (GPSR), stakeholders should consider:
-
European standards published in the Official Journal of the European Union (OJEU).
-
European standards not yet published in the OJEU, as well as international and national standards.
-
International agreements.
-
Voluntary certification schemes or similar third-party conformity assessment frameworks.
-
Commission recommendations or guidelines on product safety assessment.
-
Sector-enforced state-of-the-art technologies or product safety codes for good practice.
-
Reasonable consumer expectations regarding safety.
-
Safety requirements adopted in acts implemented by the European Commission that will be covered by European standards listed in the OJEU. Choosing certified chips ensures compliance and reliability for your lighting application.
Manufacturer Reputation
The reputation of the manufacturer plays a significant role in the quality and durability of an smd led chip. Reputable manufacturers consistently produce high-quality components. They invest in research and development, ensuring their chips offer superior performance. Key indicators of a reputable manufacturer include:
-
Being an Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) LED chip supplier.
-
Being chosen by major car manufacturers globally.
-
Providing components that deliver superior performance. Selecting a chip from a trusted manufacturer minimizes risks and ensures a reliable lighting solution for your strip lighting or other LED chip lighting project. This choice impacts the overall quality and longevity of your lighting.
Practical Integration of SMD LED Chips
Successfully integrating SMD LED chips into a project requires careful planning. This includes validating performance and considering scalability for the chosen SMD LED chip. Adding transistors can allow for higher average currents through LEDs if the current circuit is insufficient.
Power Supply Compatibility
Choosing the correct power supply is crucial for any SMD LED lighting project. Different types of power supplies are compatible with SMD LED strips. These include AC-DC adapters, available in 5V and 12V versions, which convert household current to the low voltage needed for the LEDs. USB power modules offer convenience for smaller, portable applications. For battery-powered projects, Li-ion/18650 holders and LiPo battery packs provide suitable power. Matching the power supply to the specific voltage and current requirements of your SMD chip ensures optimal performance and longevity for the lighting.
Calculating Power Needs
Accurately calculating power needs prevents overloading the power supply and ensures consistent light output. First, determine the total wattage of your strip lighting. Multiply the wattage per foot (or meter) by the total length of the strip. For example, if a strip uses 5 watts per foot and you have 10 feet, the total power needed is 50 watts. Always select a power supply with a capacity at least 20% higher than your calculated total. This provides a safety margin and extends the lifespan of both the power supply and the led chip lighting. This step is vital for any led chip installation.
Mounting and Soldering
Proper mounting and soldering techniques are essential for a reliable SMD LED installation. Mount SMD chips securely to a circuit board or heat sink. This helps dissipate heat effectively. Use appropriate soldering methods, such as reflow soldering for mass production or careful hand soldering for prototypes. Ensure clean connections to prevent shorts or intermittent failures. Correct installation directly impacts the performance and durability of the led chip. For strip light installation, ensure the adhesive backing is strong and the surface is clean.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
A thorough cost-benefit analysis considers both initial investment and long-term savings. Highly efficient SMD LED lights are 20% more efficient than alternative Chip-on-Board (COB) LED lights. LED lights can last up to 50,000 hours or more. This significantly reduces the need for frequent replacements and associated maintenance costs. LED lights are highly energy-efficient. They convert electric current directly into light without excessive heat, unlike traditional lighting. This leads to lower electricity consumption and costs. Using batteries with SMD LEDs can reduce engine runtime by 60%, extending service intervals. This requires minimal maintenance every 1,500 hours and saves on servicing costs. The reduced engine runtime and extended unit lifetime contribute to a lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) for the lighting application. This makes SMD chips a cost-effective choice for many projects.
Selecting the ideal smd led chip involves balancing many critical factors. Readers must consider performance, quality, and cost for effective lighting. The perfect chip always depends on the specific application. This guide helps evaluate various lighting needs. It ensures optimal lighting results. Consider factors beyond just brightness. Each chip offers unique benefits for different lighting. Apply these criteria to choose the best chip for your project lighting. This ensures long-term satisfaction and quality lighting for any application. Confidently select the right chip for future lighting.
FAQ
What is the main difference between SMD2835 and SMD5050 chips?
SMD2835 chips offer higher efficiency and brightness for their size. SMD5050 chips provide greater overall brightness but use more power and generate more heat. Both are popular choices for various lighting applications.
Why is Color Rendering Index (CRI) important for LED lighting?
CRI measures how accurately a light source shows true colors. High CRI (80-90+) is crucial for applications needing precise color representation, like art galleries. It ensures objects appear vibrant under the lighting.
How does thermal management affect an LED chip’s lifespan?
Effective thermal management dissipates heat efficiently. Poor heat dissipation raises the chip’s temperature, reducing its efficiency and shortening its lifespan. Proper cooling ensures long-lasting, consistent lighting.
What does “luminous efficacy” mean for LED lighting?
Luminous efficacy measures how much visible light an LED produces per unit of power. Higher efficacy means more light for less energy, making the LED more efficient. This reduces energy costs for all lighting.
Can I use any power supply with my SMD LED strip lighting?
No, you must match the power supply’s voltage and current to the LED strip’s requirements. Incorrect power can damage the LEDs or cause dim lighting. Always check specifications for safe and optimal lighting.

