
eMMC is a non-volatile, embedded memory system. It integrates Flash memory and a controller. This makes it a cost-effective, reliable mass storage device. A specialized, ruggedized version, known as industrial eMMC, is designed for demanding operational environments. Industrial applications require robust storage solutions. Power loss protection is paramount. This blog clarifies: what is industrial eMMC? It contrasts it with standard eMMC. It also explains why power loss protection is indispensable for its reliability in industrial settings.
Key Takeaways
-
Industrial eMMC is a tough memory system. It works well in harsh places. It has better parts and can handle extreme heat or cold.
-
Industrial eMMC lasts longer than regular eMMC. It can write and erase data many more times. This makes it very reliable for important jobs.
-
Power Loss Protection (PLP) is very important for industrial eMMC. It stops data from getting lost or broken if the power suddenly goes out.
-
PLP uses special parts to keep the eMMC working for a short time. This lets it save all important data safely before it shuts down.
-
Using industrial eMMC with PLP helps systems run smoothly. It means less fixing and less time when machines are not working. This saves money and keeps things safe.
What is Industrial eMMC?

Defining Industrial eMMC
eMMC stands for embedded MultiMediaCard. It represents a non-volatile memory system. This system integrates Flash memory and a Flash memory controller. This integration simplifies application interface design. It also makes eMMC a cost-effective and reliable embedded mass storage device. It combines NAND flash memory, a controller, and an interface into one compact package. Its small form factor, often the size of a postage stamp, saves valuable PCB space. Miniature versions are particularly suitable for compact devices like industrial displays.
Industrial eMMC Characteristics
Industrial eMMC possesses several key characteristics. These features ensure its suitability for demanding environments. It offers long-term durability, which is essential for continuous operation. It includes advanced wear leveling algorithms. These algorithms distribute data writes evenly across the flash memory cells. This extends the lifespan of the device. Error correction code (ECC) mechanisms detect and correct data errors. This maintains data integrity. Power-loss protection is another critical feature. It safeguards data during unexpected power interruptions.
Industrial eMMC devices adhere to specific technical specifications. These specifications define their robust performance:
|
Specification |
Details |
|---|---|
|
eMMC Standard |
JEDEC eMMC 5.1 (HS400), backward compatible |
|
Capacities |
Ranging from 4GB to 256GB |
|
Package Dimensions |
Examples include 11.5x13x0.8mm, 9.0×7.5×0.8mm, 11.5x13x0.9mm, 11.5x13x1.0mm |
|
NAND Type |
MLC and 3D TLC |
|
Operating Temperature |
-40°C to +85°C |
|
Controller Functions |
ECC, wear-leveling, IOPS optimization, read sensing |
These characteristics make industrial eMMC a robust solution for critical applications.
How Industrial eMMC Differs from Standard eMMC
Industrial eMMC stands apart from its standard, consumer-grade counterpart through several critical distinctions. These differences ensure industrial eMMC meets the rigorous demands of specialized applications.
Component Grade Differences
Industrial-grade eMMC utilizes superior components compared to consumer-grade versions. Manufacturers select industrial-grade NAND flash and controllers for their enhanced durability and reliability. Consumer eMMC often employs Triple-Level Cell (TLC) or Quad-Level Cell (QLC) NAND for cost-effectiveness. Industrial eMMC, however, primarily uses Single-Level Cell (SLC) or Multi-Level Cell (MLC) NAND. These types offer higher endurance.
|
Feature |
Industrial Grade |
Consumer Grade |
|---|---|---|
|
NAND Flash Components |
Primarily SLC (Single-Level Cell) or MLC (Multi-Level Cell) with high endurance. |
Primarily TLC (Triple-Level Cell) or QLC (Quad-Level Cell) for cost-effectiveness. |
|
Endurance (P/E Cycles) |
Higher (e.g., 60,000-100,000 for SLC, 3,000-10,000 for MLC). |
Lower (e.g., 500-3,000 for TLC, 100-1,000 for QLC). |
|
Operating Temperature Range |
Wider (e.g., -40°C to +85°C). |
Narrower (e.g., 0°C to +70°C). |
|
Data Retention |
Better, especially under extreme temperatures and power loss. |
Adequate for typical use, but less robust in harsh conditions. |
|
Error Correction Code (ECC) |
More advanced and robust ECC algorithms (e.g., LDPC). |
Standard ECC algorithms. |
|
Power Loss Protection (PLP) |
Often includes hardware-based PLP (capacitors) to protect data during unexpected power loss. |
Typically relies on firmware-based PLP, less effective than hardware. |
|
Firmware |
Optimized for consistent performance, reliability, and data integrity in demanding environments. |
Optimized for general performance and cost. |
|
Controller |
Robust controllers designed for stability, wear leveling, and error management in continuous operation. |
Controllers focused on maximizing speed and capacity at lower costs. |
|
Testing and Validation |
Rigorous and extensive testing for reliability, durability, and compatibility in specific industrial applications. |
Standardized testing for general consumer use. |
|
Bill of Materials (BOM) Control |
Strict BOM control to ensure consistent components and performance over time. |
Components may change frequently based on availability and cost, leading to potential performance variations. |
|
Lifespan and Availability |
Longer product lifecycles and guaranteed long-term availability. |
Shorter product lifecycles, components may become obsolete quickly. |
|
Cost |
Higher due to premium components, rigorous testing, and specialized features. |
Lower due to mass production and cost-optimized components. |
|
Target Applications |
Industrial automation, embedded systems, medical devices, transportation, military, critical infrastructure. |
Personal computers, laptops, gaming consoles, general consumer electronics. |
|
Performance Consistency |
Designed for sustained, consistent performance under heavy workloads and varying conditions. |
Performance can be optimized for burst speeds, but may degrade under sustained heavy loads. |
|
Vibration and Shock Resistance |
Often designed with enhanced resistance to vibration and shock. |
Standard resistance, not typically designed for extreme physical stress. |
|
Security Features |
May include advanced security features like hardware encryption, secure erase, and write protection. |
Basic security features, if any. |
|
Wear Leveling |
Advanced dynamic and static wear-leveling algorithms to extend lifespan. |
Standard wear-leveling algorithms. |
|
Over-provisioning |
Higher over-provisioning to improve endurance and performance. |
Lower over-provisioning to maximize usable capacity. |
|
Certification |
May meet specific industrial or military certifications (e.g., MIL-STD). |
Typically meets general consumer electronics standards (e.g., CE, FCC). |
Industrial eMMC typically offers capacities ranging from 1GB to 128GB. Consumer eMMC, conversely, often provides larger capacities, from 2GB to 512GB, prioritizing storage volume over extreme durability.
Temperature Range Differences
Operating temperature ranges represent a significant divergence. Consumer eMMC generally functions within a narrower range, typically 0°C to +70°C. Industrial eMMC, however, withstands much harsher conditions.
-
Industrial eMMC operates reliably from -40°C to +85°C.
-
For example, ATP’s SLC-based E800Pi e.MMC carries an industrial temperature rating of -40°C to 85°C.
-
Delkin Industrial eMMC also specifies a range of -40°C to +85°C.
-
Digi’s industrial temperature range CC6 variants operate between -40°C and 85°C.
This wider temperature tolerance makes industrial eMMC suitable for extreme environments.
Endurance and Lifespan
Industrial eMMC boasts superior endurance and a longer lifespan. This comes from its higher Program/Erase (P/E) cycles. SLC NAND, often found in industrial-grade eMMC, offers 60,000 to 100,000 P/E cycles. MLC NAND provides 3,000 to 10,000 cycles. Consumer-grade TLC or QLC NAND offers significantly fewer cycles, ranging from 100 to 3,000. This difference directly translates to how long the device can reliably store and rewrite data.
Advanced Firmware Features
Industrial eMMC integrates advanced firmware features for enhanced reliability. These include sophisticated wear-leveling, robust error correction code (ECC), and efficient bad block management.
Wear-leveling techniques are crucial for extending the lifespan of flash memory. A built-in microcontroller within the eMMC device handles these techniques. This makes wear leveling transparent to the user.
Two primary wear-leveling algorithms are commonly implemented:
-
Dynamic: This algorithm moves only data that changes over time. It leaves static data in its original blocks. It is simpler and best suited when a small percentage of flash memory holds static data. However, it does not utilize the entire storage capacity.
-
Static: This more complex algorithm intentionally relocates static data. It ensures all blocks of the flash memory wear evenly. This extends the lifespan of the storage device by using all available memory.
Industrial eMMC firmware also incorporates advanced ECC algorithms, such as LDPC (Low-Density Parity-Check). These algorithms detect and correct data errors more effectively. This maintains data integrity even under challenging conditions.
Rigorous Testing and Validation
Industrial eMMC undergoes more stringent testing and validation processes. These processes ensure reliability and longevity in demanding applications.
-
The JEDEC e.MMC 5.1 Standard (JESD84-B51) provides a compliance standard for eMMC devices. It ensures interoperability and quality, including specifications for performance, reliability, and security features.
-
The IEC 60068 standard is relevant for environmental testing of industrial eMMC devices.
-
ISO 26262 may apply for automotive safety, depending on the specific application.
Manufacturers also employ internal testing protocols.
-
A Rapid Diagnostic Test (RDT) evaluates product reliability under extreme temperatures. This includes thermal cycling tests at low (-40°C) and high (85°C) temperatures. It catches early and latent defects.
-
Automated Final Screening uses specialized machines for high-speed automated initialization and screening. This identifies errors and failed parts before packaging.
These rigorous tests guarantee the industrial grade eMMC meets the highest standards for performance and durability.
Why Power Loss Protection is Crucial
Data Corruption Risks
Unexpected power loss poses a significant threat to data integrity in industrial systems. Data corruption can occur when an eMMC device loses power during critical operations. For example, eMMC devices are susceptible to failures if powered down during a write or erase cycle. This is similar to how SD cards can fail. Unexpected power outages prevent cached data from writing to the storage media. This leads to data loss.
Consider a real-world scenario: a pharmaceutical plant experienced this issue. A lightning strike caused a gateway power outage. The plant lost GMP production records. This resulted in a failed audit. Such incidents highlight the severe consequences of data corruption.
How PLP Functions
Power Loss Protection (PLP) is a vital feature designed to prevent data corruption during unexpected power interruptions. PLP typically uses onboard capacitors. These capacitors store enough energy to power the industrial eMMC device for a short period after the main power supply fails. This brief power supply allows the eMMC controller to complete any ongoing write operations. It flushes all data from its volatile cache to the non-volatile flash memory. This ensures data integrity.
Here is how long PLP can sustain power for data flushing:
|
NAND Flash Operation |
Typical Duration |
Maximum Duration |
|---|---|---|
|
Read (Page) |
76 (μs) |
<120 (μs) |
|
Program (Page) |
820 (μs) |
<3500 (μs) |
|
Erase (Block) |
15 (ms) |
<30 (ms) |
|
ATP’s HW+FW PLP |
50 (ms) |
>80 (ms) |
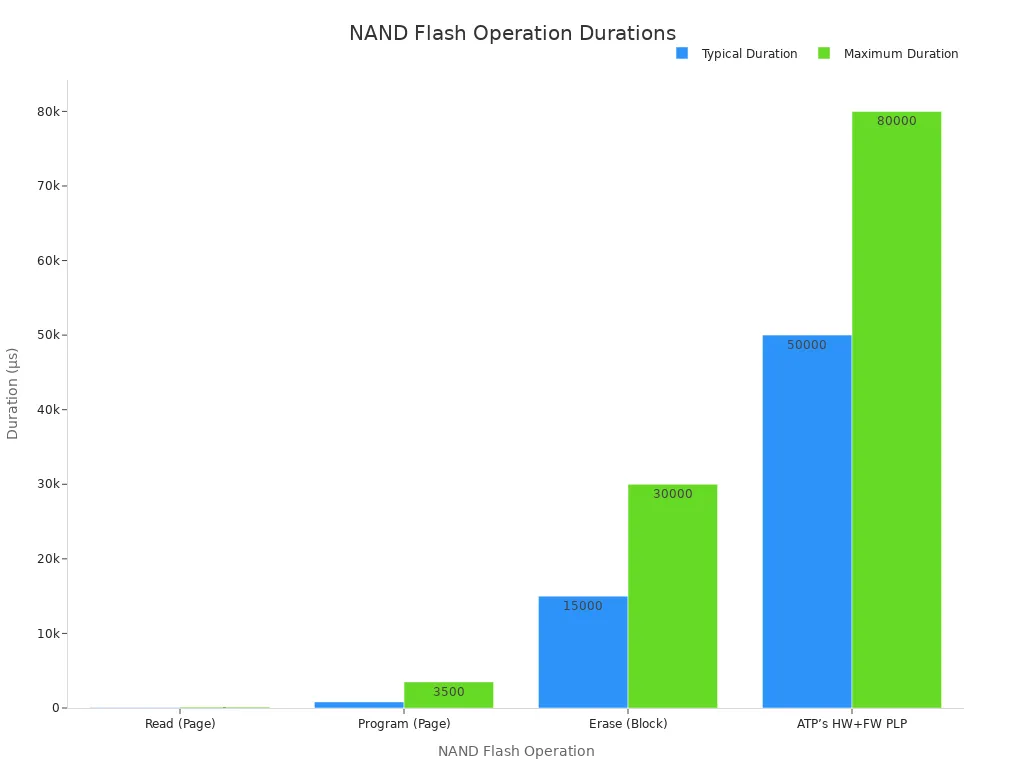
This chart shows that PLP provides sufficient time for critical operations to finish safely.
Impact of Lacking PLP
Without robust PLP, industrial systems face significant risks. Data loss becomes a common problem. Systems can become unbootable if critical operating system files corrupt. This leads to costly downtime. In some cases, a lack of PLP can cause permanent damage to the storage device itself. This requires complete replacement. The absence of PLP compromises system reliability. It also increases maintenance costs and operational risks.
Key Applications Benefiting from PLP
Many industrial applications critically depend on PLP for continuous and safe operation. These include:
-
Healthcare: Operating theaters in hospitals rely on stable systems. Power failure could jeopardize patient safety by incapacitating life-support machines.
-
Water Treatment: UV lights in water treatment plants must function without interruption.
-
Transportation: Radar equipment for airports needs constant reliability.
-
Energy and Utilities: Booster systems in pipeline applications and emergency lighting systems require uninterrupted data integrity.
-
Manufacturing: Industrial Control Systems (e.g., Safety Instrumented Systems, PLCs, PACs, DCSs) are vital. Manufacturing plants experience costly delays when downtime disrupts entire production lines.
-
Infrastructure: Facility Control Systems (e.g., building management systems, energy management and control systems) manage critical building functions.
-
Communication: Industrial Networks & Communication (e.g., Ethernet, IIoT, remote telemetry units, security systems with video cameras) handle essential data flow.
-
Control Rooms: Utility, manufacturing, transportation facilities, and security offices depend on continuous data recording and access.
Other critical sectors benefiting from PLP include:
-
Data centers
-
Financial institutions
-
Government facilities
-
Wastewater treatment
-
Engine Manufacturing Assembly Lines
These environments cannot tolerate data loss or system failure. PLP ensures these critical systems remain operational and secure.
Benefits of Industrial eMMC with PLP
Enhanced Data Integrity
Industrial eMMC with Power Loss Protection (PLP) significantly boosts data integrity. PLP ensures data being processed or cached in volatile memory, like DRAM, securely writes to non-volatile flash memory. This process greatly reduces the risk of data corruption during unexpected power loss. On-board polymer tantalum capacitors provide supplemental power. This power fully saves data in transit to NAND flash. The circuit maintains power to the NAND during programming, even if system power interrupts. This ensures data integrity, prevents data loss, and reports any resulting errors to the host system.
Extended Lifespan in Harsh Environments
Industrial eMMC devices are built for durability in challenging conditions. They offer an extended lifespan. Manufacturers implement tailored thermal solutions. These devices operate reliably beyond standard industrial temperature ranges. Robustness against shock and vibration is also achieved. Some industrial eMMC products comply with MIL-STD-810G standards. High-endurance NAND series, such as SLC, pSLC, MLC, and TLC, are utilized. Customized spare block (OP) settings further extend the lifespan. This design ensures the industrial emmc performs reliably over many years.
Reduced Maintenance and Downtime
The enhanced reliability of industrial eMMC with PLP directly leads to reduced maintenance and downtime. Systems avoid data corruption and device failures. This minimizes the need for costly repairs or replacements. Operators experience fewer interruptions. This keeps critical industrial processes running smoothly. Businesses save money and improve operational efficiency.
Industry Compliance
Industrial eMMC solutions often meet specific industry standards and certifications. This compliance is crucial for sectors with strict regulations. Examples include medical, automotive, and defense industries. Adhering to these standards ensures safety, reliability, and interoperability. It also helps businesses meet regulatory requirements.
Industrial eMMC offers superior durability, a wider operating temperature range, and advanced features compared to standard versions. Power Loss Protection (PLP) is a fundamental differentiator. It ensures data integrity and system reliability in demanding industrial applications. Choosing industrial storage with robust PLP is a strategic decision. It ensures the stability, longevity, and safety of critical industrial systems.
FAQ
What makes industrial eMMC different from standard eMMC?
Industrial eMMC uses higher-grade components. It operates in wider temperature ranges. It also offers superior endurance and advanced firmware. These features ensure reliability in demanding industrial settings.
Why is power loss protection (PLP) essential for industrial eMMC?
PLP prevents data corruption during unexpected power outages. It uses capacitors to provide temporary power. This allows the eMMC controller to finish writing data safely. This protects critical industrial data.
What are the consequences of not having PLP in industrial applications?
Without PLP, systems risk data loss and corruption. This can lead to unbootable devices and costly downtime. It compromises system reliability and increases maintenance needs.
Can industrial eMMC withstand extreme temperatures?
Yes, industrial eMMC is designed for extreme temperatures. It typically operates from -40°C to +85°C. This wide range makes it suitable for very hot or very cold industrial environments.
How does PLP protect data during a power failure?
PLP uses onboard capacitors. These capacitors store energy. They provide enough power for the eMMC controller to complete any ongoing write operations. This flushes all cached data to non-volatile memory.
See Also
MC9S12XEQ512CAL: Automotive to Industrial Control Applications Explored In-Depth
Efficient Power Management Solutions: Discovering the LPQ252-CEF Module’s Capabilities
MC9S12XET512VAG Microcontroller: Automotive System Integration Strategies and Practical Insights
NXP Microcontrollers: Powering Automotive Electronics with In-Depth Analysis and Applications
ARTESYN NPT42-M: Essential Power Solutions for Industrial Automation Systems

