The Intel FJ8071504741823 Processor N100 gains significant traction in compact, low-power computing solutions. Its relevance grows in 2025. This budget-friendly processor raises a central question: can it truly deliver performance and efficiency for modern demands? The FJ8071504741823S RMDM Intel chip offers a compelling proposition. This analysis provides a data-driven exploration, helping readers make informed decisions about its capabilities and value.
Key Takeaways
-
The Intel N100 processor is good for small computers. It uses little power and costs less money.
-
This processor works well for daily tasks. You can browse the internet, use office programs, and watch videos easily.
-
The N100 is great for home servers and network devices. It uses very little electricity, even when running all the time.
-
It has some limits. The N100 is not for playing advanced games or editing complex videos. It is best for simple jobs.
-
The N100 saves energy. This means lower electricity bills and less heat. It is a smart choice for many users.
Intel Processor N100 Key Specifications:

Architecture and Core Details:
The Intel FJ8071504741823 Processor N100 features a robust design for efficient computing. It incorporates four cores, providing solid performance for its class. This processor reaches a maximum turbo frequency of 3.40 GHz. It also includes 6 MB of Intel Smart Cache, which helps speed up data access. This architecture allows the N100 to handle various tasks while maintaining low power consumption.
Integrated Graphics Overview:
The Intel N100 integrates capable graphics directly onto the chip. This integrated graphics solution handles everyday visual tasks effectively. It supports high-resolution displays and smooth video playback. Users can expect good performance for web browsing, office applications, and streaming media. The graphics unit also supports dual 4K displays, enhancing productivity for many users.
Memory and Storage Support:
The Intel FJ8071504741823 Processor N100 offers flexible memory options. It supports both DDR4 and DDR5 memory types. The processor accommodates a maximum memory size of 16 GB. Users can choose between DDR4 3200 MT/s, DDR5 4800 MT/s, or LPDDR5 4800 MT/s. The highest officially supported memory speed is 4800 MT/s. This versatility allows system builders to optimize for cost or performance. For storage, systems often pair the N100 with fast NVMe SSDs, ensuring quick boot times and application loading.
Connectivity and I/O:
Systems featuring the Intel N100 typically offer comprehensive connectivity. They include modern wireless options like Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E and Bluetooth 5.1, 5.2, or 5.3. These features ensure fast and reliable wireless communication. For wired connections, many N100-based devices provide 2.5G Gigabit Ethernet. Available ports often include USB-C, USB-A (ranging from 2.0 to 3.2 Gen2), and HDMI. Some configurations also feature Thunderbolt 4 Type-C ports with DisplayPort 1.4. A 3.5mm headphone/microphone combo jack and MicroSD card readers are also common.
N100 Performance Benchmarks:
The Intel N100 processor undergoes rigorous testing. These tests reveal its capabilities across various computing tasks. Benchmarks provide a clear picture of its performance. They help users understand what to expect from this low-power chip.
Synthetic CPU Benchmarks:
Synthetic benchmarks measure the raw processing power of the Intel N100. These tests push the CPU to its limits. The N100 achieves impressive scores for its class. It processes 7,197 Thousand Strings/Sec. It handles data at 4,028 MBytes/Sec. Memory operations reach 57,692 KBytes/Sec. The processor renders 389 Frames/Sec in specific tests. It also performs 2,919 Million Matrices/Sec.
Geekbench 6 provides further insights. The N100 scores 1,204 in single-core performance. Its multi-core score reaches 2,314. These numbers demonstrate the processor’s efficiency. They show its ability to manage multiple tasks simultaneously.
Real-World Application Performance:
Synthetic scores offer a baseline. Real-world application performance shows how the N100 handles daily tasks. The processor performs well in common scenarios. It provides a responsive experience for many users.
|
Application Category |
Intel N100 Performance |
Comparison / Notes |
|---|---|---|
|
Office Applications |
Sufficient for daily tasks |
Comparable to older Core i5/i7 CPUs (e.g., i5-7200U) |
|
Web Browsing |
Smooth experience |
Handles multiple tabs and multimedia content well |
|
Light Content Creation |
Capable for basic photo editing and video playback |
Not designed for heavy rendering or complex video editing |
|
General Responsiveness |
Good for a low-power chip |
Provides a snappy feel for everyday use |
The Intel N100 handles office suites and web browsing with ease. It supports multiple browser tabs and multimedia content smoothly. For light content creation, such as basic photo editing or video playback, it performs capably. However, it does not suit heavy rendering or complex video editing. Users find its general responsiveness good for a low-power chip. This provides a snappy feel for everyday use. Despite strong synthetic scores, real-world performance sometimes falls short of a full-fledged i5 processor. An i5 offers more power for demanding applications.
Integrated Graphics and Gaming:
The N100 includes integrated graphics. This unit handles visual tasks. Testing often involves systems with 12GB DDR5 RAM. This memory configuration helps the integrated graphics perform better. The N100 can play various new and old games. It runs older titles and less demanding modern games at lower settings. Users can enjoy casual gaming and media consumption. It streams high-definition video without issues.
Storage and Network Throughput:
Storage and network performance significantly impact user experience. Systems with the N100 often feature fast NVMe SSDs. These drives provide quick boot times and rapid application loading. This enhances the overall responsiveness of the system. Many N100-based devices also include 2.5G Gigabit Ethernet. This offers faster network speeds. It improves data transfer for home servers or network-attached storage (NAS) setups.
N100 vs. Alternatives in 2025:
The Intel FJ8071504741823 Processor N100 stands out among its peers. It offers a strong balance of performance and efficiency. When compared to the N150, the N100 typically performs better. It shows 5-15% faster results in multi-thread tests. This advantage is noticeable during prolonged CPU benchmarks. In 2025, the N100 remains a competitive option. It targets users needing a budget-friendly, low-power processor. It excels in specific use cases where efficiency is key.
N100 Real-World Usage Scenarios:
The Intel N100 processor excels in many practical applications. Its design focuses on efficiency and compact size. This makes it suitable for various computing needs.
Mini-PCs for Everyday Tasks:
Mini-PCs powered by the Intel N100 have become popular for daily computing. These small devices handle common tasks efficiently. Users can browse the web with multiple tabs open. They can also use office applications like word processing, spreadsheets, and presentations. Email management is smooth. The N100 even supports light photo editing. It streams 4K video content without issues.
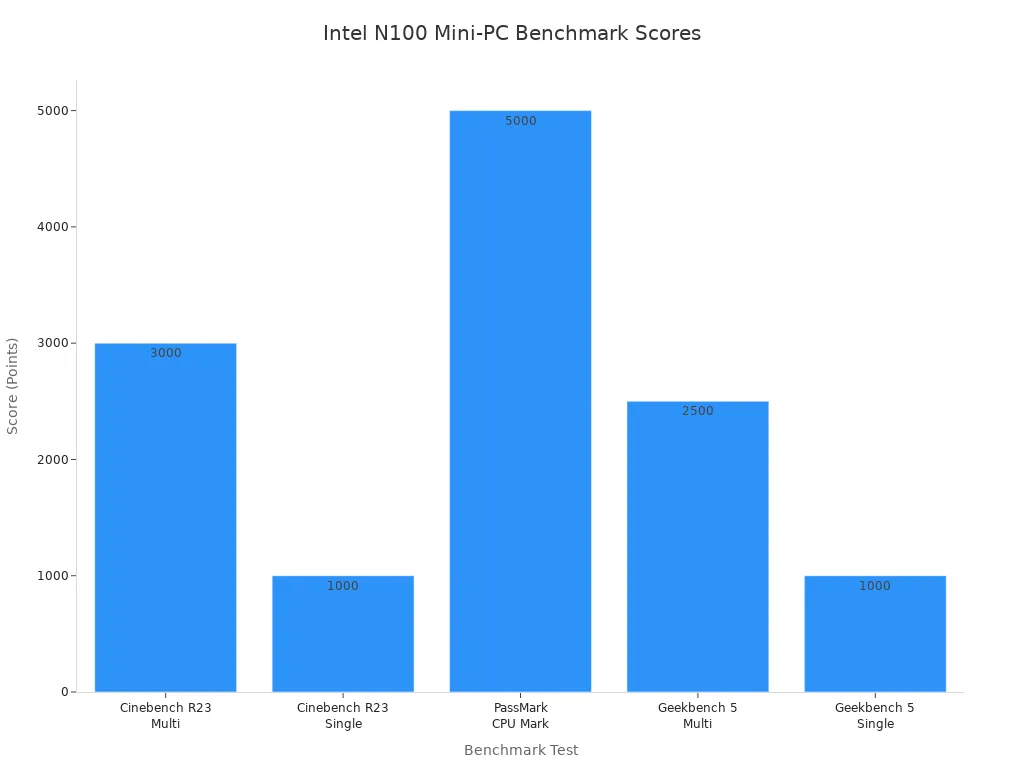
The N100’s performance metrics confirm its capability for these tasks. It achieves around 3000 points in Cinebench R23 Multi-core tests. Its single-core score reaches approximately 1000 points. PassMark CPU Mark shows about 5000 points. Geekbench 5 reports roughly 2500 for multi-core and 1000 for single-core performance. The processor has 4 cores and 4 threads. It boosts up to 3.4 GHz. Its integrated Intel UHD Graphics, with 24 EUs, operates up to 750 MHz. This allows for good visual performance. The low TDP of 6W makes these mini-PCs very energy efficient.
Home Server and NAS Builds:
The Intel N100 is an excellent choice for home server and Network Attached Storage (NAS) builds. Its low power consumption makes it ideal for 24/7 operation. An entire system built around the N100 can consume as little as 5W at idle. Under load, the total system power draw typically stays below 20W. This is very efficient for its performance class. It offers a cost-effective solution for home server deployments.
The N100 also provides robust virtualization support. It includes VT-x, VT-d, EPT, and VPID. This comprehensive feature set is crucial for home servers. It allows users to run multiple virtual machines or containers efficiently. VT-d is especially beneficial. It enables passing through hardware like network cards or storage controllers directly to virtual machines. This enhances performance and flexibility. Users can set up virtualized firewalls like pfSense or dedicated NAS operating systems. The processor features 4 E-cores and 4 threads. It has a base clock of 1.0 GHz and a max turbo frequency of 3.4 GHz.
|
Feature |
Intel N100 |
|---|---|
|
Cores |
4 (E-cores) |
|
Threads |
4 |
|
Base Clock |
1.0 GHz |
|
Max Turbo Frequency |
3.4 GHz |
|
TDP |
6W |
|
Idle Power |
~5W (entire system) |
|
Load Power |
~15-20W (entire system) |
|
Virtualization |
VT-x, VT-d, EPT, VPID (full support) |
Router and Firewall Appliances:
The Intel N100 is highly suitable for dedicated router and firewall appliances. Its network throughput capabilities are impressive. It achieves around 2.35 Gbit/s per 2.5GbE port. A system with four 2.5GbE ports can reach a total throughput of approximately 9.4 Gbit/s. This is more than enough for most home and small business environments.
The Intel N100 is highly suitable for dedicated router and firewall appliances. Its network throughput capabilities, demonstrated by achieving around 2.35 Gbit/s per 2.5GbE port and a total of approximately 9.4 Gbit/s across four ports, are more than adequate for most home and small business environments. The processing capabilities, with low CPU utilization even under full network load and strong OpenSSL performance, indicate it can handle routing, firewall rules, and VPN tasks efficiently. Furthermore, its low power consumption makes it an excellent choice for always-on appliances.
The processor’s capabilities ensure efficient handling of network tasks. CPU utilization remains low, even under full network load, typically around 20-30% with four 2.5GbE ports. It also shows strong OpenSSL performance. It processes AES-256-CBC at about 1.5 GB/s and SHA256 at roughly 1.8 GB/s. Its low power consumption, around 6.5W at idle and 10-12W under load, makes it an excellent choice for always-on appliances.
|
Metric |
Value |
|---|---|
|
2.5GbE Throughput (iperf3) |
~2.35 Gbit/s per port |
|
Total Throughput (4x 2.5GbE) |
~9.4 Gbit/s |
|
Power Consumption (Idle) |
~6.5W |
|
Power Consumption (Load) |
~10-12W (with 4x 2.5GbE at full load) |
|
CPU Utilization (Load) |
~20-30% (with 4x 2.5GbE at full load) |
|
OpenSSL Speed (AES-256-CBC) |
~1.5 GB/s |
|
OpenSSL Speed (SHA256) |
~1.8 GB/s |
Digital Signage and Kiosk Use:
The Intel N100 processor also finds its place in digital signage and kiosk applications. Its compact size allows for easy integration into various display units. The low power consumption ensures cost-effective operation, especially for devices running continuously. The integrated graphics can drive high-resolution displays, making it suitable for displaying advertisements, information, or interactive content. Its reliability and minimal heat output are crucial for these unattended systems.
Thin Clients and Education:
In educational settings and corporate environments, the N100 serves as an ideal processor for thin clients. Thin clients rely on remote servers for processing power. The N100 provides enough local processing to handle the remote desktop protocols smoothly. Its energy efficiency reduces operating costs for large deployments. The low cost of N100-based devices makes them budget-friendly for schools and businesses. They offer a reliable and secure way to access centralized resources.
Power Consumption and Efficiency:
Power Draw and TDP:
The Intel N100 processor distinguishes itself with remarkable power efficiency. It boasts a very low Thermal Design Power (TDP) of just 6 watts. This minimal TDP signifies that the processor generates very little heat during operation. Consequently, it requires a small amount of electrical power to function effectively. Systems incorporating the N100 consume significantly less electricity compared to computers using more powerful central processing units. This characteristic makes the N100 an excellent option for devices designed for continuous, always-on operation. For instance, mini-PCs and home servers greatly benefit from this inherent low power draw, reducing their operational costs.
Thermal Management:
The N100’s 6-watt TDP directly influences its thermal management capabilities. This low heat output allows for the implementation of passive cooling solutions. Many devices built around the N100 can operate entirely without fans. Fanless designs offer several distinct advantages. They ensure completely silent operation, which is highly desirable in environments like living rooms, bedrooms, or quiet office spaces. Furthermore, fanless systems prevent dust accumulation inside the device’s chassis. This enhances overall reliability and extends the hardware’s operational lifespan. The absence of moving parts, such as cooling fans, also significantly reduces the risk of mechanical failure.
Energy Cost-Benefit:
The Intel N100’s low power consumption translates into tangible and significant energy cost savings for users. Over an extended period, these savings can accumulate substantially, particularly for devices that run continuously, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. Users will observe a noticeable reduction in their monthly electricity bills. This makes the N100 an economically sound and attractive choice for both budget-conscious individual consumers and small businesses. Beyond the financial advantages, the processor’s inherent energy efficiency also contributes positively to a smaller carbon footprint. This aligns well with increasing global environmental concerns. The N100 therefore offers a compelling balance between practical performance and ecological responsibility.
Intel N100 Pros and Cons in 2025:
Key Advantages:
The Intel N100 processor offers several compelling benefits in 2025. Its cost-effectiveness stands out. Users often find N100-powered mini PCs priced under $200. This makes it a very budget-friendly option for many. The processor also boasts impressive power efficiency. It operates with a low Thermal Design Power (TDP) of just 6 watts. This minimal power consumption often allows for fanless designs. Such designs lead to silent operation and reduced energy bills. The N100’s low power and heat generation enable a compact form factor. This makes it ideal for very small device designs, including mini PCs and embedded systems. It features 4 efficient cores, providing solid performance for its intended uses.
Identified Limitations:
Despite its strengths, the Intel N100 has some limitations. It is not designed for heavy, demanding tasks. For example, intense gaming or professional video editing will push its limits. Users needing high-end graphics or complex computations should look elsewhere. The N100’s integrated graphics are suitable for casual use, not high-performance gaming. Many N100-based mini PCs offer limited upgradeability. Users cannot easily change components like the CPU or GPU. This restricts future performance enhancements. Its performance, while good for its class, does not match that of higher-end Intel Core i5 or i7 processors.
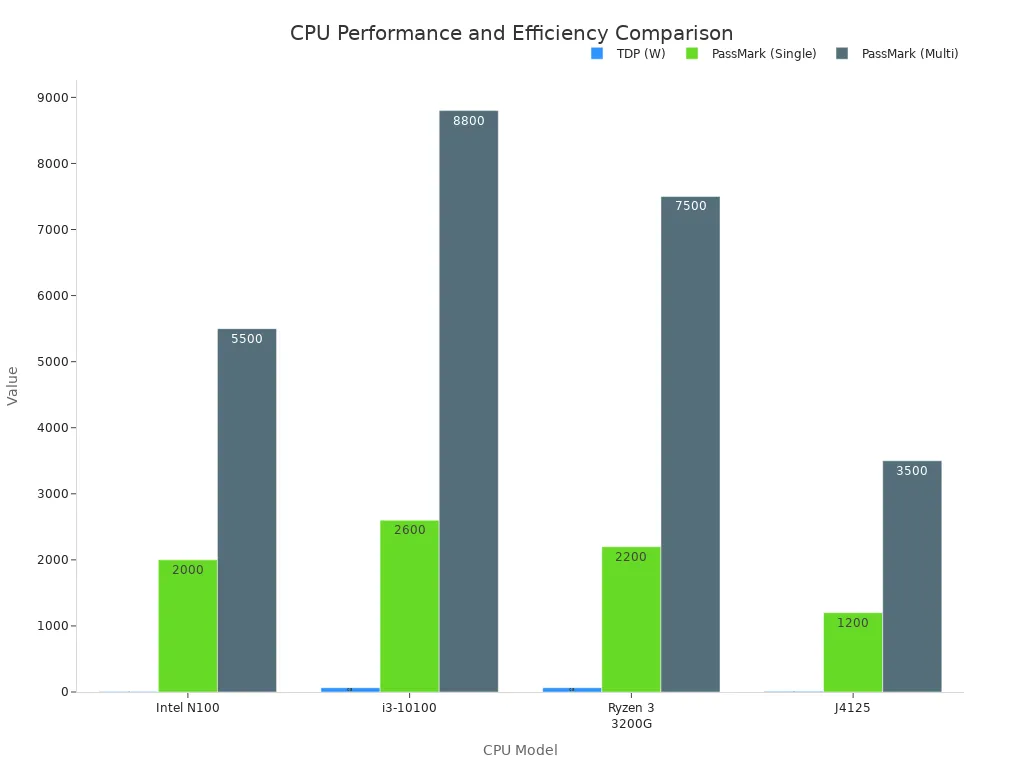
The Intel N100 remains a compelling choice in 2025. It excels for mini-PCs, home servers, and network appliances. Its value proposition balances cost, performance, and efficiency. The N100 operates at a very low 6W TDP. This makes it significantly more power-efficient than alternatives like the i3-10100 (65W). Systems featuring the N100 are generally highly affordable. They offer strong performance-per-dollar for their target uses.
Buyers seeking efficient, budget-friendly solutions will find it ideal. The future looks bright for such low-power processors. Share your experiences below!
FAQ
Is the Intel N100 suitable for gaming?
The Intel N100 is not designed for demanding games. Its integrated graphics can handle older titles or very light modern games at low settings. Users should not expect high-performance gaming from this processor. It excels more in everyday tasks and media consumption.
What are the ideal use cases for the Intel N100?
The Intel N100 shines in specific roles. It is excellent for mini-PCs handling daily tasks like web browsing and office work. It also performs well in home servers, NAS builds, and dedicated router/firewall appliances. Digital signage and thin clients also benefit from its efficiency.
Can the Intel N100 run Windows 11 effectively?
Yes, the Intel N100 can run Windows 11 effectively. It meets the minimum system requirements for the operating system. Users will experience smooth performance for general computing tasks. The processor provides a responsive environment for everyday Windows 11 usage.
How does the Intel N100 compare to an Intel Core i5 processor?
The Intel N100 is a low-power, budget-friendly processor. It offers good performance for its class. An Intel Core i5 processor provides significantly more power and better performance for demanding applications. The N100 focuses on efficiency and cost, while an i5 targets higher performance needs.
See Also
Xilinx XC7K325T-2FFG676C: Practical Implementation for Next-Generation Networks
MC9S12XEQ512CAL: Automotive to Industrial Control Applications Deep Dive
EP2C50F484I8N FPGA: Unlocking High-Performance Embedded System Design Possibilities
NXP Microcontrollers: Core Power for Automotive Electronics and Practical Applications
MC9S12XET512VAG Microcontroller: Automotive System Integration Strategy and Practice


