Choosing the right battery often depends on key factors like voltage, chemistry, and compatibility. For example:
-
LR44 Battery: Nominal voltage of 1.5 volts and uses zinc and manganese oxide chemistry.
-
LIR44 Battery: Rechargeable with lithium-based chemistry and a similar voltage to LR44.
-
LIR2032 Battery: Lithium-ion coin cell with 3.6 volts and a 40mAh capacity.
The LR44 battery, a type of LR44 cylindrical alkaline button cell battery, operates using a chemical reaction between zinc and manganese oxide. In contrast, lithium-based LIR batteries deliver higher voltage and better longevity. Understanding these differences ensures safety and optimal device performance.
Key Takeaways
-
LR44 batteries are cheap and work well for small devices. These include watches and calculators. They run at 1.5 volts but can’t be recharged.
-
LIR44 batteries are eco-friendly and rechargeable. They have the same voltage as LR44. They cut down waste and save money over time.
-
LIR2032 batteries give more power with 3.6 volts. They work for high-power devices like computer motherboards. Check if your device can use them.
-
Using rechargeable batteries saves money and helps the environment. Always make sure the battery fits your device.
-
Handle and store batteries carefully to stay safe. Follow the maker’s rules to avoid leaks or overheating.
Overview of LR44, LIR44, and LIR2032

Understanding the differences between LR44, LIR44, and LIR2032 batteries helps users select the right power source for their devices. Each battery type offers unique features, specifications, and applications.
LR44 Battery Overview
The LR44 battery is a widely used alkaline button cell. It operates at 1.5 volts and is known for its reliability and long lifespan. Commonly found in watches, calculators, and small electronic devices, this battery is a popular choice for everyday applications.
Key specifications include:
-
Battery Type: Alkaline
-
Voltage: 1.5V
-
Common Uses: Watches, calculators, small electronics
-
Equivalents: AG13, A76, G13, LR1154, L1154, 154
-
Silver-Oxide Equivalents: SR44, SR44SW, SR44W, SB-B9, 303, 357
The LR44 battery’s versatility and affordability make it a go-to option for many devices.
LIR44 Battery Overview
The LIR44 battery is a rechargeable alternative to the LR44. It uses lithium-ion chemistry, which provides a similar voltage while offering the advantage of reusability. This battery is ideal for users seeking a more sustainable option.
Key features include:
-
Rechargeable: Yes
-
Voltage: Comparable to LR44
-
Chemistry: Lithium-ion
-
Applications: Similar to LR44, including watches and small electronics
The LIR44 battery reduces waste and offers long-term savings, making it an eco-friendly choice for compatible devices.
LIR2032 Battery Overview
The LIR2032 battery is a lithium-ion coin cell with a higher voltage and capacity compared to LR44 and LIR44. Its compact design and rechargeable nature make it suitable for modern electronics.
|
Feature |
Details |
|---|---|
|
Energy |
0.144Wh |
|
Dimension |
20*3.2mm |
|
Charge |
Yes |
|
Operating Temperature |
-20 to +60℃ |
|
Capacity |
40mAh |
|
Voltage |
3.6V |
|
Application Scope |
Computer motherboards, calculators, watches, electronic thermometers, medical instruments |
|
Key Features |
High performance, long-lasting, rechargeable, compact design |
The LIR2032 battery’s higher voltage and capacity make it suitable for devices requiring more power, such as computer motherboards and medical instruments.
Key Differences Between LR44, LIR44, and LIR2032
Chemistry and Voltage Comparison
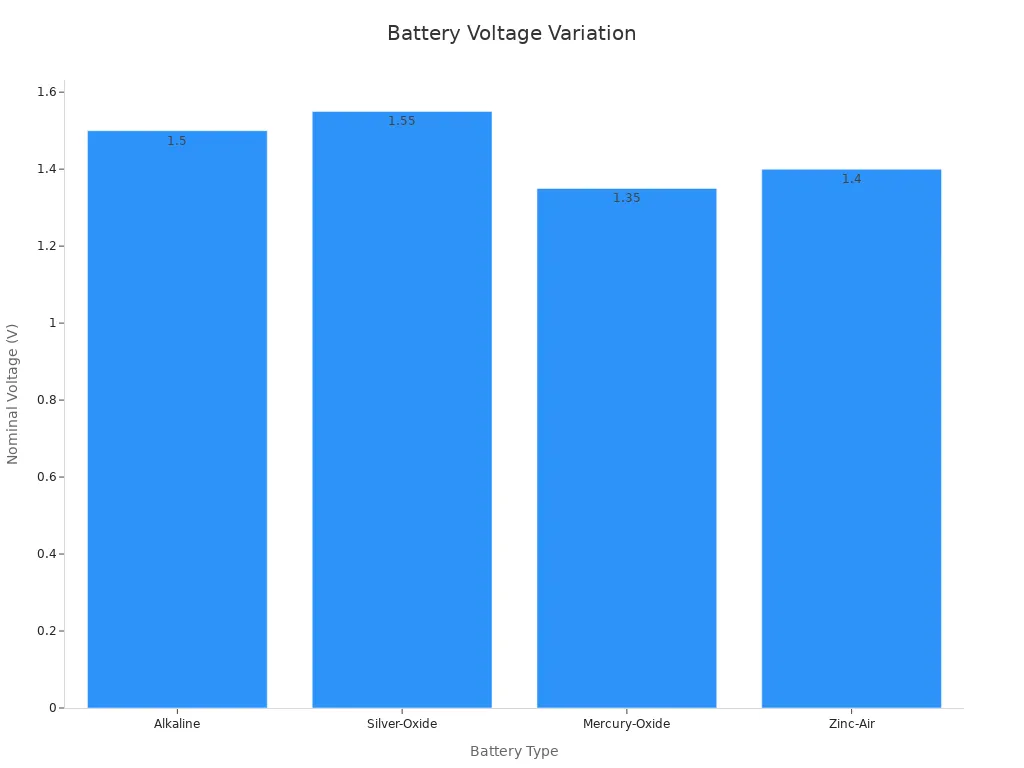
The chemistry and voltage of a battery determine its performance and compatibility with devices. The LR44 battery uses alkaline chemistry, which relies on a reaction between zinc and manganese oxide. This chemistry provides a nominal voltage of 1.5V. In contrast, the LIR44 battery employs lithium-ion chemistry, offering a similar voltage but with the added benefit of rechargeability. The LIR2032 battery, another lithium-ion option, delivers a higher nominal voltage of 3.6V, making it suitable for devices requiring more power.
|
Battery Type |
Nominal Voltage |
Chemistry |
|---|---|---|
|
LR44 (Alkaline) |
1.5V |
Zinc and manganese oxide |
|
LIR44 (Lithium-ion) |
3.6V |
Lithium-ion |
|
LIR2032 (Lithium-ion) |
3.6V |
Lithium-ion |
Alkaline batteries, like the LR44, provide less stable voltage compared to lithium-ion batteries. Lithium-ion batteries maintain a more consistent voltage throughout their discharge cycle, which benefits devices requiring steady power. The chart below illustrates the nominal voltage differences across various battery chemistries:
Capacity and Lifespan Analysis
Battery capacity and lifespan are critical factors for users seeking long-lasting performance. The LR44 battery has a capacity of approximately 120mAh, which is sufficient for low-drain devices like watches and calculators. However, its lifespan depends on usage and cannot be recharged. The LIR44 battery offers a similar capacity but can be recharged multiple times, extending its overall usability. The LIR2032 battery, with a capacity of 40mAh, is designed for devices requiring higher voltage rather than extended runtime.
|
Parameter |
LR44 |
LIR44 |
LIR2032 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Capacity |
120mAh |
~120mAh |
40mAh |
|
Voltage Rated |
1.5V |
3.6V |
3.6V |
|
Chemistry |
Alkaline |
Lithium-ion |
Lithium-ion |
The LR44 battery’s capacity makes it ideal for short-term use in low-power devices. Rechargeable options like the LIR44 and LIR2032 provide long-term savings by reducing the need for frequent replacements. However, their capacity may not match that of non-rechargeable alkaline batteries in certain applications.
Rechargeability and Reusability Insights
Rechargeability is a key advantage of lithium-ion batteries like the LIR44 and LIR2032. These batteries can be recharged hundreds of times, reducing waste and offering significant cost savings over time. In contrast, the LR44 battery is disposable, contributing to environmental concerns when discarded improperly.
The global push for sustainable energy solutions highlights the importance of rechargeable batteries. Lithium-ion batteries, including the LIR44 and LIR2032, support this initiative by enabling reuse and reducing the demand for raw materials. Studies show that recycling lithium-ion batteries can recover valuable metals like cobalt, nickel, and copper, further minimizing environmental impact.
|
Battery Type |
Recoverable Metals (per kg of <3 mm fraction) |
|---|---|
|
Ni-Cd |
390 g Ni, 330 g Cd |
|
Ni-MH |
630 g Ni, 80 g Co |
|
Li-ion |
250 g Co, 110 g Ni, 120 g Cu |
The LR44 battery, while affordable, lacks the reusability of lithium-ion alternatives. Users seeking eco-friendly options should consider rechargeable batteries to reduce waste and promote sustainability.
Compatibility and Use Cases
Devices Commonly Using LR44 Batteries
The LR44 battery is a versatile power source found in a wide range of devices. Its compact size and reliable performance make it suitable for both everyday and specialized applications. Common devices that use LR44 batteries include:
-
Digital thermometers
-
Calculators
-
Flashlights
-
Laser pointers
-
Hearing aids
-
Security system components
-
Memory backup configurations
These devices benefit from the LR44 battery’s stable voltage and long shelf life. For example, digital thermometers rely on the consistent power output of LR44 batteries to ensure accurate readings. Similarly, calculators and laser pointers require the compact design and dependable energy supply that this battery provides.
Compatibility of LIR44 and LIR2032 with Devices
The LIR44 and LIR2032 batteries offer rechargeable alternatives to traditional disposable batteries. However, their compatibility depends on the voltage and power requirements of the device. The LIR44 battery, with its lithium-ion chemistry, can replace the LR44 battery in many devices, provided the device supports rechargeable batteries. This makes it a sustainable option for watches, small electronics, and other low-drain devices.
The LIR2032 battery, on the other hand, is a coin cell with a higher voltage of 3.6V. It is commonly used in devices that require more power, such as computer motherboards, medical instruments, and electronic thermometers. The table below highlights the types of devices compatible with these batteries:
|
Battery Type |
Common Devices Used In |
|---|---|
|
LR43 |
Watches, Calculators, Toys, Alarm Transmitters, Small Electronics |
|
LR44 |
Medical Devices, LED Lights, Keyless Entry Systems, Digital Thermometers, Garage Door Openers |
|
LR41 |
Digital Thermometers, Flashlights, Medical Devices, Calculators, Laser Pens |
When switching to rechargeable options like the LIR44 or LIR2032, users must verify the device’s voltage requirements and ensure it supports lithium-ion chemistry. Using an incompatible battery can damage the device or result in suboptimal performance.
Switching to Rechargeable Alternatives: Key Considerations
Switching to rechargeable batteries offers several benefits, including reduced waste and long-term cost savings. However, users should consider several factors before making the transition. The table below compares key considerations for rechargeable and disposable batteries:
|
Key Consideration |
Rechargeable Batteries |
Disposable Batteries |
|---|---|---|
|
Corrosion Resistance |
Generally more corrosion-proof materials |
Prone to leakage and corrosion |
|
Performance |
Better capacity and shelf life |
Consistent power until depletion |
|
Usage Scenarios |
Not recommended for smoke alarms and low-power devices |
Preferred for low-power draw devices like wall clocks and flashlights |
Rechargeable batteries like the LIR44 and LIR2032 are ideal for devices with moderate to high power consumption. They are less suitable for low-drain devices, such as wall clocks, where disposable batteries like the LR44 battery perform better. Additionally, users should invest in a compatible charger and follow proper charging practices to maximize the lifespan of rechargeable batteries.
Tip: Before switching to rechargeable batteries, check the device manual for compatibility information. This ensures optimal performance and prevents potential damage.
Cost and Environmental Impact

Comparing Upfront Costs and Long-Term Savings
The cost of batteries varies significantly between disposable and rechargeable options. Disposable batteries, such as the lr44 battery, may seem affordable initially but can accumulate high costs over time due to frequent replacements. Rechargeable batteries, on the other hand, require a higher upfront investment but offer substantial savings in the long run.
|
Battery Type |
Cost (Approx.) |
Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
|
Disposable Batteries |
> $1000 |
High due to disposal issues |
|
Rechargeable Batteries |
$16.47 |
Lower due to longer lifecycle |
Economic studies highlight the financial advantages of rechargeable batteries. Lithium-ion systems, for instance, have upfront costs ranging from $300–$750/kWh. However, they reduce electricity bills and even allow users to sell stored energy back to the grid. These systems typically break even within 7–12 years, making them a cost-effective choice for long-term use.
Environmental Benefits of Rechargeable Batteries
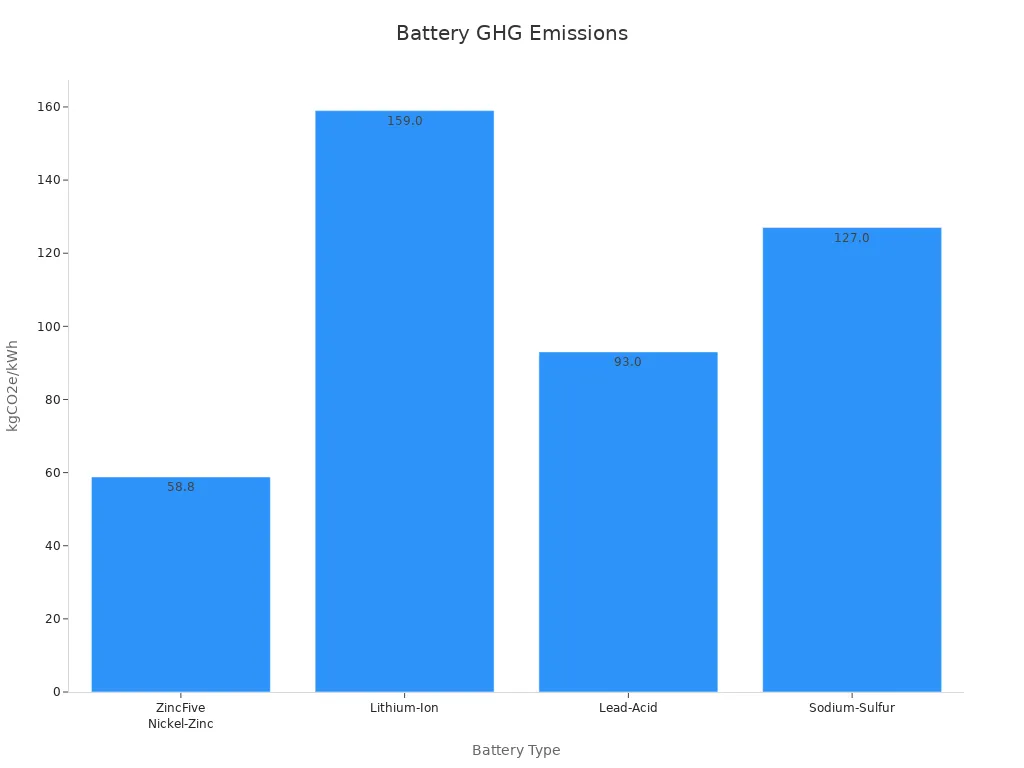
Rechargeable batteries significantly reduce environmental impact compared to disposable ones. Their longer lifecycle minimizes waste, while recycling programs recover valuable materials like cobalt and nickel. Environmental assessments reveal that lithium-ion batteries emit 159 kgCO2e/kWh, whereas newer technologies like ZincFive Nickel-Zinc reduce emissions by 63%.
|
Environmental Indicator |
ZincFive Nickel-Zinc |
Lithium-Ion |
Lead-Acid |
Sodium-Sulfur |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
GHG Emissions (kgCO2e/kWh) |
58.8 |
159.0 |
93.0 |
127.0 |
|
Reduction Compared to Lithium-Ion |
63% |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Reduction Compared to Lead-Acid |
37% |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Reduction Compared to Sodium-Sulfur |
54% |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
Rechargeable batteries also contribute to a circular economy by reducing the demand for raw materials and promoting sustainable energy practices.
Proper Disposal and Recycling Practices
Proper disposal and recycling of batteries are essential to minimize environmental harm. Disposable batteries, including the lr44 battery, should never be thrown in regular trash due to the risk of chemical leakage. Instead, users should take them to designated recycling centers. Rechargeable batteries, while more eco-friendly, also require responsible recycling to recover valuable metals and prevent pollution.
Many manufacturers and retailers offer take-back programs for used batteries. These programs ensure safe disposal and help recover materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. By participating in such initiatives, users can contribute to reducing landfill waste and conserving natural resources.
Safety Considerations
Voltage Differences and Device Safety
Voltage differences between battery types can significantly impact device safety. Using a battery with a higher voltage than recommended may damage sensitive components or cause overheating. For example, lithium-ion batteries like the LIR2032, with a nominal voltage of 3.6V, are unsuitable for devices designed for 1.5V alkaline batteries like the LR44. This mismatch can lead to electrical hazards, including short circuits or thermal risks.
-
Multimeters are rated for specific voltage levels, with low-end models safe up to 600 volts and advanced ones up to 1000 volts.
-
Stored electrical energy in batteries can produce flammable hydrogen gas, especially in poorly ventilated areas.
-
Toxic or corrosive electrolytes in batteries require personal protective equipment (PPE) and engineering controls to ensure safety.
Proper ventilation and adherence to device voltage requirements are essential to prevent accidents. Users should always consult device manuals to confirm compatibility before switching battery types.
|
Safety Standard |
Description |
|---|---|
|
UN38.3 |
Ensures batteries are safe during transport, including tests for short-circuit, impact, and heat exposure. |
|
RoHS |
Restricts the use of specific hazardous materials in batteries. |
|
REACH |
Addresses the environmental impact of batteries. |
|
CCC |
Required for exporting to China, ensuring safety and quality. |
|
IEC Standards |
Globally recognized standards for battery safety and performance. |
Risks Associated with Overcharging Rechargeable Batteries
Overcharging rechargeable batteries poses severe risks, including thermal runaway and fire hazards. A study by FSRI and UL Solutions demonstrated the dangers of overcharging lithium-ion batteries. The experiments revealed that overcharging could lead to thermal runaway within 65 minutes, resulting in flaming combustion and potential explosions. In a closed environment, the time from smoke detection to a gas explosion was as short as 20 seconds.
Key Insight: Overcharging can cause rapid temperature increases, leading to catastrophic failures. Users should always follow manufacturer-recommended charging rates and durations to mitigate these risks.
Handling and Storage Best Practices
Proper handling and storage of batteries are critical for safety and longevity. Physical damage to batteries can result in leaks or explosions, while improper storage increases the risk of degradation. To ensure safety:
-
Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
-
Use protective covers during transport to prevent short circuits.
-
Keep batteries at approximately 50% charge for long-term storage.
|
Key Recommendations |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Charging Instructions |
Follow recommended charging rates and durations to prevent overcharging. |
|
Usage Conditions |
Operate batteries within specified temperature and humidity ranges. |
|
Maintenance Procedures |
Perform regular maintenance for rechargeable batteries. |
|
Compatibility Information |
Use only compatible devices and accessories to avoid electrical mismatches. |
Adhering to these best practices minimizes risks and ensures optimal battery performance over time.
Understanding the differences between LR44, LIR44, and LIR2032 batteries helps users make informed choices. LR44 batteries suit low-drain devices due to their affordability and reliability. LIR44 batteries offer rechargeability, reducing waste and long-term costs. LIR2032 batteries provide higher voltage for power-intensive devices.
Recommendation: Choose LR44 for cost-effective solutions, LIR44 for eco-friendly options, and LIR2032 for high-performance needs.
Compatibility and safety remain crucial. Users should verify device requirements and follow proper handling practices to ensure optimal performance and avoid risks.
What is the main difference between LR44 and LIR44 batteries?
LR44 batteries are disposable alkaline cells with 1.5V voltage. LIR44 batteries are rechargeable lithium-ion cells with similar voltage but offer reusability. LIR44 batteries reduce waste and save money over time, while LR44 batteries suit low-drain devices needing occasional replacements.
Can LIR2032 batteries replace LR44 batteries?
No, LIR2032 batteries cannot replace LR44 batteries. LIR2032 batteries have a higher voltage (3.6V) and different dimensions. Using them in devices designed for LR44 batteries may cause damage or safety issues. Always check device compatibility before switching battery types.
How many times can rechargeable batteries like LIR44 be reused?
Rechargeable batteries like LIR44 can typically be recharged hundreds of times. Their lifespan depends on usage, charging practices, and storage conditions. Proper care ensures maximum reusability and long-term savings compared to disposable alternatives.
Are rechargeable batteries better for the environment?
Rechargeable batteries reduce waste and conserve resources. They last longer and can be recycled to recover valuable materials like lithium and cobalt. Disposable batteries contribute to landfill waste, making rechargeable options more eco-friendly.
What safety precautions should users follow when handling batteries?
Users should store batteries in cool, dry places and avoid exposing them to extreme temperatures. Rechargeable batteries should not be overcharged. Always use compatible chargers and follow manufacturer guidelines to prevent risks like leaks, overheating, or short circuits.
See Also
M30280FAHP: A Trustworthy Option for Medical Integrated Circuits
Reasons to Select Coilcraft XPL2010 for VRM and VRD
Explore LPQ252-CEF for Optimal Power Management Solutions
SN74LVC4245APW: A Simple Guide to Sensor Integration
Comparing STM32F401VCT6 and STR750FV2T6 in Medical Devices