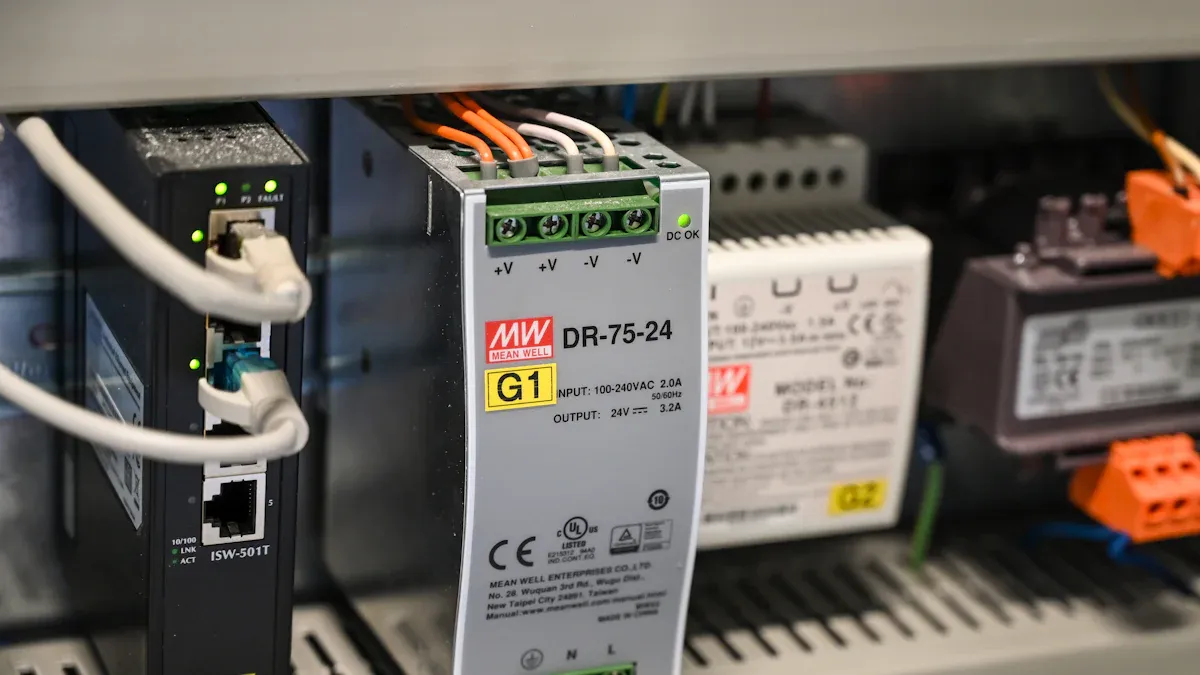
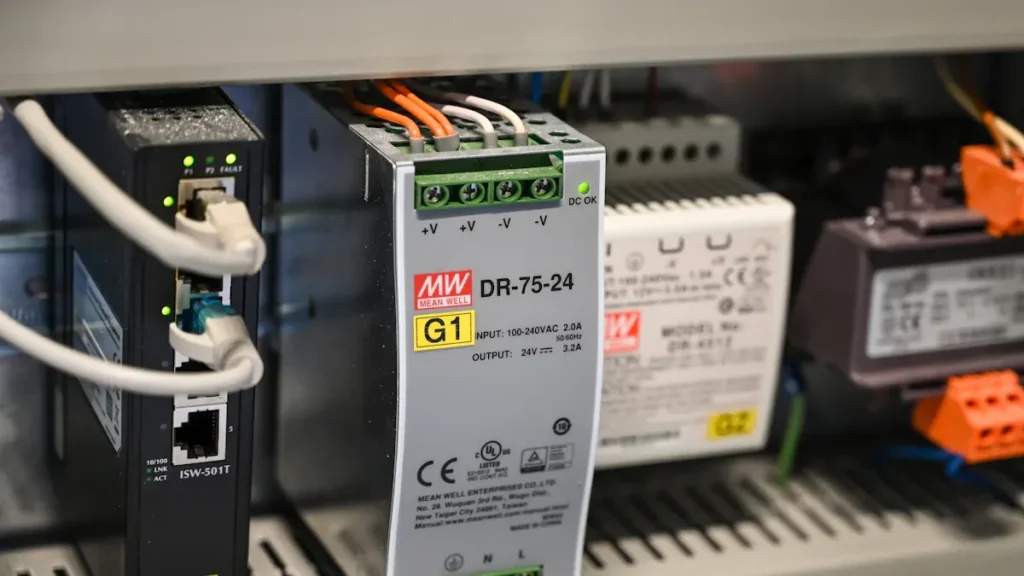
A smps power supply is an advanced electronic device designed to convert electrical power with remarkable efficiency. It achieves this by rapidly switching the input voltage on and off, which minimizes energy loss and reduces heat generation. This design makes it an ideal choice for applications requiring compact, reliable, and energy-efficient power solutions.
Efficiency levels of smps power supplies often surpass 90%, making them vital for energy conservation in industries like automotive and telecommunications.
Smps power supplies offer several advantages over traditional linear power supplies. These include higher energy efficiency, compact size, and reduced operational costs. They also ensure stable voltage output, even under varying load conditions, which enhances their reliability and lifespan.
Key Takeaways
-
Switch mode power supplies (SMPS) change electrical power quickly. They switch voltage on and off fast, saving energy with over 90% efficiency.
-
SMPS are smaller and lighter than older power supplies. This makes them great for small devices like phones and laptops.
-
These power supplies give steady voltage output. They work well even if the load changes.
-
SMPS can use both AC and DC inputs. This makes them useful for many electronics and industrial tools.
-
Important industries using SMPS include healthcare, cars, and communication. These fields need energy-saving and dependable systems.
Basic Concept of a Switch-Mode Power Supply

What is an SMPS Power Supply
A switched-mode power supply (SMPS) is an electronic device that efficiently converts electrical power. It uses a switching regulator to transfer energy from an input source, such as AC or DC, to a load while adjusting voltage and current levels. Unlike linear power supplies, which dissipate excess energy as heat, SMPS minimizes energy loss by rapidly switching the input voltage on and off. This process ensures efficient power conversion and reduces heat generation.
The design of an SMPS incorporates key components like transformers, capacitors, and inductors. These components enable the device to operate at high frequencies, typically ranging from 20 kHz to several MHz. This high-frequency operation allows for smaller transformer sizes, resulting in a compact and lightweight design. Additionally, SMPS can handle a wide range of input voltages, making it versatile for various applications.
Key Features of Switched-Mode Power Supplies
Switched-mode power supplies offer several features that make them superior to traditional power supplies. These include:
-
High Efficiency: SMPS achieves efficiency levels of 90% or higher, significantly reducing energy waste compared to linear regulators, which typically operate at around 30% efficiency.
-
Compact Design: The use of high-frequency switching reduces the size of transformers and other components, making SMPS smaller and lighter.
-
Regulated Output: Feedback mechanisms ensure stable voltage output, even under varying load conditions.
-
Wide Input Voltage Range: SMPS can operate with both AC and DC inputs, accommodating a broad range of voltage levels.
-
Noise Suppression: Advanced designs, such as Silent Switcher® architecture, minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI), allowing SMPS to function near sensitive devices without performance degradation.
-
Reliability: Built-in protection features, such as over-voltage and over-current safeguards, enhance the durability and safety of SMPS.
These features make switched-mode power supplies an ideal choice for applications requiring efficiency, reliability, and compactness.
Why SMPS is More Efficient than Linear Power Supplies
The efficiency of a power supply is determined by the ratio of energy consumed to energy supplied. SMPS outperforms linear power supplies due to its ability to minimize energy losses. Linear power supplies dissipate excess energy as heat through a pass transistor, leading to significant energy waste. In contrast, SMPS uses a switching element to regulate current flow, reducing active component losses.
|
Metric/Trend |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Energy Efficiency |
SMPS are known for superior efficiency compared to linear power supplies, reducing energy waste. |
|
Operational Costs |
Higher efficiency ratings lead to reduced operational costs and improved product performance. |
|
Compact Design |
Smaller transformers and components make SMPS lightweight and space-saving. |
Manufacturers optimize SMPS designs by incorporating fast-switching components like MOSFETs and bipolar transistors. These components enable high-frequency operation, which reduces transformer size and improves thermal management. Additionally, noise suppression techniques, such as EMI noise shields, enhance efficiency by minimizing output ripple voltage. These advancements ensure that SMPS remains the preferred choice for modern electronic devices.
How a Switch-Mode Power Supply Works
Key Components of a Switch-Mode Power Supply
A switch-mode power supply relies on several critical components to achieve efficient power conversion. Each component plays a specific role in ensuring the device operates effectively. Below is a breakdown of these components and their functions:
|
Component |
Function |
|---|---|
|
TOP224P |
Acts as the switching regulator, controlling the flow of energy. |
|
VDz1 |
Clamps spike voltage caused by leakage inductance, protecting the circuit. |
|
VD1 |
Rectifies and filters the voltage from the secondary winding. |
|
C2, L1, C3 |
Work together to produce a stable 12V output voltage. |
|
R2, VDz2 |
Provide a dummy load to improve load regulation. |
|
L2 |
Reduces common-mode leakage current, enhancing safety and performance. |
|
C7 |
Filters interference from coupling capacitance. |
|
C5 |
Filters peak current on the control terminal, ensuring smooth operation. |
These components work in harmony to convert electrical energy efficiently while maintaining a compact design. Their integration allows switched-mode power supplies to deliver stable and reliable performance across various applications.
Operational Principles of Switched-Mode Power Supplies
Switched-mode power supplies operate by rapidly switching the input voltage on and off to regulate energy flow. This process involves several stages:
-
Input Rectification and Filtering: The input voltage, whether AC or DC, passes through a rectifier circuit. This circuit converts AC to DC and filters out noise or fluctuations.
-
High-Frequency Switching: A switching regulator, such as a MOSFET, alternates the current flow at high frequencies. This rapid switching minimizes energy loss and reduces heat generation.
-
Voltage Transformation: The high-frequency current passes through a transformer. The transformer adjusts the voltage level to match the requirements of the connected load.
-
Output Rectification and Filtering: The transformed voltage is rectified and filtered again to produce a stable DC output. Capacitors and inductors play a crucial role in this stage.
-
Feedback Control: A feedback loop monitors the output voltage. If the voltage deviates from the desired level, the regulator adjusts the switching frequency or duty cycle to maintain stability.
Tip: The high-frequency operation of switched-mode power supplies allows for smaller transformers and components, making them compact and lightweight.
This operational principle ensures that switched-mode power supplies deliver efficient and regulated power, even under varying load conditions.
Advantages of the SMPS Power Supply Design
The design of a switch-mode power supply offers several advantages over traditional power supplies. These benefits make it a preferred choice for modern electronic devices:
|
Comparative Advantage |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Synchronous Rectification |
Replaces diodes with MOSFETs, reducing conduction losses and improving efficiency. |
|
Integrated Components |
Minimizes circuit area and parasitic losses, enhancing overall performance. |
|
Low Quiescent Current |
Reduces power loss during low-load conditions, ideal for battery-powered devices. |
|
Pulse Skipping |
Increases efficiency at light loads by skipping unnecessary switching cycles. |
These features contribute to the superior performance of switched-mode power supplies. For instance, synchronous rectification significantly reduces energy waste, while integrated components allow for a more compact design. Low quiescent current and pulse skipping further enhance efficiency, particularly in devices that operate under varying load conditions.
The combination of these advantages ensures that switched-mode power supplies remain a reliable and efficient solution for powering modern electronics.
Types of Switch-Mode Power Supplies

Switch-mode power supplies can be classified into two main categories: isolated and non-isolated converters. Each type serves specific applications and offers unique advantages based on its design and functionality.
Isolated Converters (e.g., Flyback, Forward)
Isolated converters use a transformer to transfer energy between the input and output circuits. This design provides galvanic isolation, ensuring electrical separation for safety and noise reduction. Two common types of isolated converters are flyback and forward converters.
-
Flyback Converter: This converter stores energy in the transformer during the “on” phase and releases it during the “off” phase. Its simple design makes it cost-effective and suitable for low-power applications like charging stations and smart home devices. Flyback converters dominate the isolated converter market, holding approximately 60% of the share.
-
Forward Converter: Unlike the flyback converter, the forward converter transfers energy directly through the transformer during the “on” phase. It offers higher efficiency and is ideal for industrial equipment and data centers requiring stable power delivery.
Note: The isolated converter market is projected to grow from $655.6 million in 2024 to $909.1 million by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.6%.
Non-Isolated Converters (e.g., Buck, Boost, Buck-Boost)
Non-isolated converters do not use a transformer, making them more compact and efficient for applications where isolation is unnecessary. These converters regulate voltage by directly connecting the input and output circuits.
-
Buck Converter: This converter steps down a higher input voltage to a lower output voltage. It is widely used in battery charging, LED lighting, and voltage regulation.
-
Boost Converter: This type increases the output voltage above the input voltage. It is commonly found in USB charging ports and high-intensity LED systems.
-
Buck-Boost Converter: This versatile converter can either step up or step down the voltage, depending on the input and output requirements. It is ideal for applications needing flexible voltage adjustment.
|
Type of SMPS |
Description |
Applications |
|---|---|---|
|
Buck Converter |
Converts higher input voltage to lower output voltage. |
Battery charging, voltage regulation, LED lighting. |
|
Boost Converter |
Increases output voltage above input voltage. |
Powering high-intensity LEDs, USB charging ports. |
|
Buck-Boost Converter |
Regulates output voltage that can be higher or lower than input voltage. |
Applications needing voltage adjustment. |
Non-isolated converters are preferred for their simplicity and efficiency in compact electronic devices. Their design minimizes energy loss, making them a popular choice for modern power systems.
Applications of Switched-Mode Power Supplies
Switched-mode power supplies play a crucial role in powering modern devices across various industries. Their high efficiency, compact design, and ability to handle diverse voltage requirements make them indispensable in consumer electronics, industrial systems, medical equipment, and more.
Consumer Electronics and IT Hardware
Switched-mode power supplies have revolutionized the consumer electronics and IT hardware sectors. Their ability to minimize energy loss while maintaining compact designs has made them the preferred choice for powering everyday devices.
-
The demand for consumer electronics has driven significant growth in the switch-mode power supply transformers market.
-
Almost all electronic devices, including mobile phones, laptops, and gaming consoles, now rely on SMPS for efficient power conversion.
-
Recent innovations in power adapters have improved conversion efficiency, enabling global energy savings in the consumer electronics industry.
For instance, SMPS ensures that devices like LED TVs and network routers operate efficiently, reducing power consumption and heat generation. This efficiency not only benefits users but also contributes to environmental sustainability.
Industrial and Medical Equipment
In industrial and medical settings, switched-mode power supplies provide reliable and regulated power for critical operations. Their ability to meet stringent safety and performance standards makes them ideal for these applications.
-
In healthcare, SMPS complies with CF leakage standards for emergency medical devices, ensuring patient safety.
-
Hospitals have adopted advanced medical power supply systems, resulting in energy savings and improved equipment reliability.
-
Smart power management systems powered by SMPS enhance operational efficiency in healthcare facilities.
Industrial equipment, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and motor control systems, also benefit from SMPS. These power supplies ensure stable voltage output, which is essential for maintaining precision and reliability in factory automation systems.
Automotive, Aerospace, and Telecommunications
The automotive, aerospace, and telecommunications industries rely heavily on switched-mode power supplies for their energy-efficient and compact designs. These industries demand high power density and reliability, which SMPS delivers effectively.
|
Aspect |
Details |
|---|---|
|
Market Value (2022) |
Approximately USD 20 billion |
|
Projected Market Value (2030) |
USD 40 billion |
|
Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) |
8.3% |
|
Key Drivers |
Increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions, proliferation of electronic devices, and advancements in technology. |
|
Efficiency Improvement |
Expected to improve by 15% over the next decade, impacting design and implementation. |
|
Importance of Power Density |
Critical for compact designs and performance, enabling smaller, efficient devices. |
In the automotive sector, SMPS powers battery management systems and infotainment devices. Aerospace applications include avionics systems and satellite power supplies, where compact and efficient designs are critical. In telecommunications, SMPS supports base station power supplies and fiber-optic networking equipment, ensuring uninterrupted communication.
Switch-mode power supplies (SMPS) transform electrical energy efficiently by using high-frequency switching techniques. Their compact design, regulated output, and ability to handle diverse voltage ranges make them indispensable in modern electronics.
SMPS plays a vital role in industries like healthcare, automotive, and telecommunications, where reliability and energy efficiency are critical.
Readers can explore SMPS to optimize power solutions for their devices. Its versatility and performance benefits make it a preferred choice for applications requiring precision and sustainability.
What is the main purpose of a switch-mode power supply (SMPS)?
An SMPS converts electrical power efficiently by using high-frequency switching. It adjusts voltage and current levels to meet the requirements of connected devices. This ensures stable power delivery while minimizing energy loss and heat generation.
How does an SMPS differ from a linear power supply?
An SMPS uses switching regulators to convert power, while a linear power supply dissipates excess energy as heat. SMPS offers higher efficiency, compact size, and better thermal management, making it more suitable for modern electronics.
Can an SMPS handle both AC and DC inputs?
Yes, most SMPS designs can operate with both AC and DC inputs. This versatility allows them to function in various applications, from consumer electronics to industrial systems.
Why is SMPS preferred for compact devices?
SMPS operates at high frequencies, reducing the size of components like transformers and inductors. This results in a smaller, lighter design, making it ideal for compact devices such as smartphones, laptops, and LED lighting systems.
What industries benefit the most from SMPS?
Industries like consumer electronics, healthcare, automotive, and telecommunications rely heavily on SMPS. Its efficiency, reliability, and compact design make it indispensable for powering devices in these sectors.
See Also
Understanding The IRF820 MOSFET For Power Management Applications
Comprehensive Guide To Using AD620AN In Television Power
Explore The LPQ252-CEF For Enhanced Power Efficiency
ARTESYN NPT42-M: Driving Automation In Industrial Settings
Three Key Benefits Of XCF01SVOG20C In Industrial Automation