TRANSISTORTO66 vs TRANSISTORTO92 electronic part number
TRANSISTORTO66 and TRANSISTORTO92 electronic parts serve different roles in electronics based on their design and capabilities. TRANSISTORTO66 features a robust structure that supports higher power and efficient heat dissipation, making it ideal for demanding applications like industrial switching and audio outputs. TRANSISTORTO92, with its compact form, suits low-power tasks such as signal processing and small device switching. Each type addresses specific requirements, enabling engineers to match the right component to their project’s needs. Understanding these differences ensures better performance and reliability in electronic systems.
Key Takeaways
TRANSISTORTO66 works well for high-power uses because it is strong and handles heat well.
TO-92 transistors are small and good for low-power jobs, great for tiny gadgets.
When picking a transistor, check its power limits and size to make it work best.
Keeping the transistors cool is important for them to last and work well.
Think about price and how easy it is to find when choosing between TRANSISTORTO66 and TO-92 for your project.
Specifications Comparison
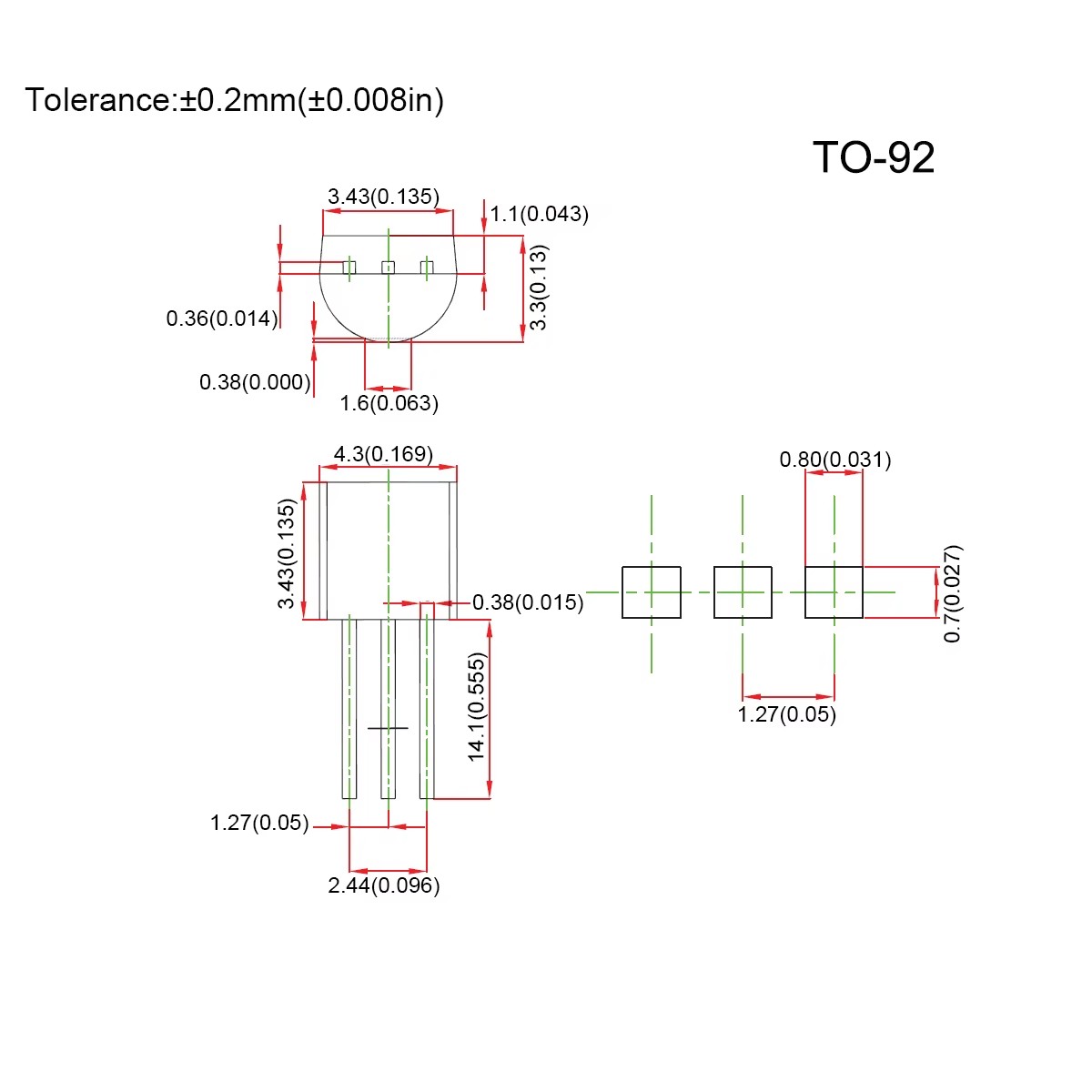
Physical Characteristics of TRANSISTORTO66 and TO-92
The physical design of a transistor plays a crucial role in its application. TRANSISTORTO66 features a larger, metallic casing that provides durability and efficient heat dissipation. Its robust structure makes it suitable for high-power applications. In contrast, the to-92 package is compact and lightweight. This design allows it to fit into small electronics where space is limited.
The to-92 component package typically consists of three leads extending from a plastic body. This standard to-92 package is easy to handle and install, making it a popular choice for low-power circuits. On the other hand, the TRANSISTORTO66 has a more complex mounting process due to its larger size and heat sink requirements. Engineers often choose between these two based on the physical constraints of their projects.
Electrical Ratings of TRANSISTORTO66 vs TO-92
Electrical ratings determine how well a transistor performs under specific conditions. TRANSISTORTO66 supports higher voltage and current levels, making it ideal for power-intensive tasks. It can handle significant loads without compromising performance. The to-92, however, is designed for low-power applications. Its electrical ratings are suitable for signal processing and general-purpose switching.
For instance, the to-92 can operate efficiently in circuits requiring minimal current. This makes it a reliable replacement for older components in small devices. Meanwhile, the TRANSISTORTO66 excels in industrial settings where high power and reliability are essential. Understanding these ratings helps engineers select the right transistor for their needs.
Thermal Performance of TRANSISTORTO66 and TO92
Thermal performance is a critical factor in choosing a transistor. TRANSISTORTO66 offers superior heat dissipation due to its metallic casing and larger surface area. This design allows it to operate efficiently in high-temperature environments. It is often used in power supplies and audio outputs where heat management is crucial.
The to-92, while compact, has limited thermal capabilities. Its plastic body restricts heat dissipation, making it suitable for low-power applications. Engineers often pair the to-92 with circuits that generate minimal heat. Despite its limitations, the to-92 remains a reliable choice for small-scale electronics.
Packaging and Mounting Options for TO-66 and TO-92
Packaging and mounting options play a vital role in determining how transistors integrate into electronic systems. The TO-66 package offers a sturdy design with a metallic casing. This casing provides durability and supports efficient heat dissipation. Engineers often mount TO-66 transistors onto heat sinks to manage thermal performance. The package includes two leads and a mounting hole, which simplifies installation in high-power circuits.
The standard to-92 package, on the other hand, features a compact plastic body. Its lightweight design makes it ideal for small-scale electronics. The to-92 component package includes three leads that extend from the body, allowing easy soldering onto circuit boards. Unlike TO-66, the to-92 does not require additional heat sinks due to its low-power nature. This simplicity makes it a popular choice for general-purpose applications.
Mounting options for TO-66 components often involve screws or clips to secure the transistor to a heat sink. This ensures stability and optimal heat transfer. In contrast, the to-92 relies on direct soldering to the board, which minimizes installation time. Engineers frequently use the to-92 as a replacement for older components in compact devices. Its versatility allows it to fit into tight spaces without compromising functionality.
The TO-66 package is better suited for industrial applications where durability and heat management are critical. The to-92 excels in consumer electronics, such as remote controls and small appliances. Both packages serve distinct purposes, enabling engineers to choose the right option based on project requirements.
Tip: When selecting a transistor package, consider the thermal demands and physical constraints of the project. For high-power applications, TO-66 provides superior performance. For low-power circuits, the to-92 offers simplicity and efficiency.
The TO-226 package, which is similar to TO-92, provides another option for compact designs. However, the TO-92 remains the preferred choice for most small-scale applications due to its widespread availability and ease of use.
Applications and Use Cases
Common Applications for TRANSISTORTO66
TRANSISTORTO66 is widely used in high-power electronic circuits due to its robust design and excellent heat dissipation capabilities. It is particularly effective in industrial switching applications, where reliability and performance under heavy loads are critical. Engineers often choose this transistor for power supplies, as it can handle significant current and voltage levels without overheating. Audio output stages also benefit from its ability to manage high power while maintaining signal integrity.
The following table highlights key specifications that make TRANSISTORTO66 suitable for these applications:
Specification | Value |
|---|---|
Maximum Operating Temperature | 175 °C |
Power Dissipation | 25 W |
Transition Frequency | 4 MHz |
Package Type | TO-66 |
Polarity/Channel Type | PNP |
Application | Switching |
These characteristics ensure that TRANSISTORTO66 performs reliably in demanding environments, making it a preferred choice for engineers working on high-power systems.
Common Applications for TO-92 Transistors
TO-92 transistors are commonly found in low-power circuits due to their compact size and ease of use. They are ideal for signal processing tasks, such as amplifiers, where minimal current is required. These transistors also excel in general-purpose switching applications, making them a versatile component in small electronic devices like remote controls and sensors.
The MPSA92 model of TO-92 transistors has proven particularly effective in amplifiers and switching circuits. Studies emphasize the importance of proper design dimensions to avoid issues like impedance variations. Effective thermal management strategies, such as optimizing PCB layouts, further enhance their reliability. These factors contribute to the widespread success of TO-92 transistors in low-power applications.
Tip: When designing circuits with TO-92 transistors, ensure proper heat dissipation to maintain performance and longevity.
Industry-Specific Use Cases for TO-66 and TO-92
In industrial settings, TRANSISTORTO66 is often used in heavy-duty equipment requiring high power and durability. Applications include motor control systems, industrial power supplies, and high-frequency switching circuits. Its ability to handle high temperatures and dissipate heat efficiently makes it indispensable in these environments.
TO-92 transistors, on the other hand, are more prevalent in consumer electronics. They are frequently used in household appliances, portable devices, and small-scale automation systems. Their compact size allows them to fit into tight spaces, making them a practical replacement for older, bulkier components.
Both transistor types serve distinct roles across industries. Engineers select TRANSISTORTO66 for its power-handling capabilities and TO-92 for its versatility in compact, low-power designs.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of TRANSISTORTO66
TRANSISTORTO66 offers several benefits that make it a preferred choice for high-power applications. Its robust metallic casing ensures excellent durability, even in demanding environments. This design also provides superior heat dissipation, allowing the transistor to operate efficiently under heavy loads. Engineers often rely on TRANSISTORTO66 for its ability to handle high voltage and current levels without compromising performance.
Another advantage is its reliability in industrial settings. TRANSISTORTO66 performs consistently in applications like power supplies and motor control systems. Its sturdy construction and high thermal tolerance make it suitable for environments where heat management is critical. These features ensure that TRANSISTORTO66 delivers long-lasting performance in high-power circuits.
Disadvantages of TRANSISTORTO66
While TRANSISTORTO66 excels in many areas, its larger size can pose challenges in compact designs. The need for additional heat sinks and mounting hardware increases the complexity of installation. This makes it less suitable for projects with strict space constraints.
The cost of TRANSISTORTO66 is another consideration. Its advanced features and robust design often result in a higher price compared to smaller transistors. Engineers must weigh these factors when selecting components for their projects.
Advantages of TO-92 Transistors
TO-92 transistors are highly valued for their compact size and versatility. Their lightweight plastic casing allows them to fit into small electronic devices, making them ideal for space-constrained designs. Engineers frequently use TO-92 as a replacement for older, bulkier components in consumer electronics.
Another advantage is their ease of use. The simple three-lead design of TO-92 simplifies installation and reduces assembly time. These transistors are also cost-effective, making them a popular choice for low-power applications like signal processing and general-purpose switching. Despite their small size, TO-92 transistors deliver reliable performance in a wide range of circuits.
Disadvantages of TO-92 Transistors
TO-92 transistors, while versatile and compact, have certain limitations that engineers must consider. One of the primary drawbacks lies in their thermal performance. The small plastic casing of the to-92 package provides limited surface area for heat dissipation. This constraint makes it unsuitable for applications that generate significant heat. Engineers often need to implement additional thermal management strategies, such as optimizing PCB layouts or using external to-92 heatsinks, to maintain reliable performance.
Another challenge with TO-92 transistors involves their physical dimensions. Variations in the size of the package can affect impedance and thermal properties. These inconsistencies may lead to performance issues in sensitive circuits. Additionally, deviations in lead spacing can introduce parasitic elements, which compromise circuit stability. Such issues require careful design considerations to ensure the transistor operates as intended.
The compact size of TO-92 transistors also limits their power-handling capabilities. They are not designed to manage high voltage or current levels, which restricts their use to low-power applications. This limitation makes them unsuitable for industrial or high-power environments where robust performance is essential.
Despite these disadvantages, TO-92 transistors remain a popular choice for small-scale electronics. Their ease of use and cost-effectiveness often outweigh their limitations in low-power designs. However, engineers must evaluate their project requirements carefully to determine if TO-92 transistors are the right fit.
Note: Proper thermal management and precise circuit design can mitigate many of the challenges associated with TO-92 transistors.
How to Choose the Right Transistor
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between TO-66 and TO-92
Selecting the right transistor involves evaluating several key factors. Engineers must consider the electrical and physical requirements of their projects to ensure optimal performance. The following table outlines critical specifications to compare when choosing between TO-66 and TO-92 transistors:
Specification | Description |
|---|---|
Maximum Voltage | The highest voltage the transistor can handle without breakdown. |
Maximum Collector Current | The maximum current that can flow through the collector terminal. |
Type | The type of transistor, either NPN or PNP. |
Maximum Power | The maximum power the transistor can dissipate without damage. |
Frequency | Important for driver transistors, less so for power supply transistors. |
TO-66 transistors are better suited for high-power applications due to their ability to handle higher voltages and currents. Their robust design also supports greater power dissipation. In contrast, TO-92 transistors are ideal for low-power circuits where compact size and simplicity are priorities. Engineers should carefully analyze these specifications to match the transistor to the demands of their project.
Tip: Always verify the transistor's type (NPN or PNP) to ensure compatibility with the circuit design.
Matching Specifications to Project Requirements
Matching a transistor's specifications to project requirements ensures reliable and efficient operation. Engineers should evaluate the technical benchmarks of their project and align them with the transistor's capabilities. For instance, TO-66 transistors excel in applications requiring high power and heat dissipation, such as industrial switching and audio outputs. TO-92 transistors, on the other hand, are better suited for low-power tasks like signal amplification and general-purpose switching.
Key considerations for matching specifications include:
Production-grade suitability: Ensure the transistor meets the quality standards for production deployment.
Performance measurement: Evaluate the transistor's performance under real-world conditions.
Thermal management: Assess the heat dissipation requirements of the circuit.
Voltage and current handling: Verify that the transistor can handle the maximum voltage and current levels of the application.
Engineers often use tools like Apache JMeter and Gatling to simulate performance and validate their choices. These tools help identify potential issues, such as overheating or impedance mismatches, before finalizing the design.
Note: Proper testing and validation are essential to ensure the transistor performs as expected in the final application.
Cost and Availability of TRANSISTORTO66 and TO-92
Cost and availability play a significant role in selecting the right transistor. TO-92 transistors are widely available and cost-effective, making them a popular choice for budget-conscious projects. Their simple design and ease of use further reduce overall project costs. TO-66 transistors, while more expensive, offer superior performance in high-power applications. Their robust construction and advanced features justify the higher price for projects requiring durability and reliability.
When considering availability, engineers should account for lead times and sourcing options. TO-92 transistors are commonly stocked by most suppliers due to their widespread use in consumer electronics. TO-66 transistors, being more specialized, may require sourcing from specific manufacturers or distributors.
Tip: For large-scale projects, consider bulk purchasing to reduce costs and ensure a steady supply of components.
By balancing cost, availability, and technical requirements, engineers can make informed decisions and select the most suitable transistor for their needs.
TRANSISTORTO66 and TRANSISTORTO92 serve distinct purposes in electronic design. TRANSISTORTO66 excels in high-power applications due to its robust construction and superior heat dissipation. TO-92, with its compact size, is ideal for low-power circuits and space-constrained designs. Each offers unique advantages tailored to specific project needs.
Selecting the right transistor enhances overall performance. Proper choices lead to improved gain characteristics, better noise margins, and low-voltage saturation. These benefits reduce errors and optimize circuit efficiency. Engineers should evaluate power requirements, thermal demands, and physical constraints to ensure compatibility.
Tip: Always match transistor specifications to project goals for reliable and efficient results.
1. What is the main difference between TRANSISTORTO66 and TO-92 transistors?
TRANSISTORTO66 handles higher power and dissipates heat efficiently due to its metallic casing. TO-92, with its compact plastic body, is better suited for low-power applications like signal processing and small electronics.
Tip: Choose TRANSISTORTO66 for high-power needs and TO-92 for compact, low-power designs.
2. Can TO-92 transistors replace TRANSISTORTO66 in circuits?
No, TO-92 transistors cannot replace TRANSISTORTO66 in high-power circuits. TO-92 lacks the power-handling and heat-dissipation capabilities required for such applications. Always match the transistor's specifications to the circuit's demands.
3. What are the typical use cases for TRANSISTORTO66?
TRANSISTORTO66 is commonly used in power supplies, industrial switching, and audio output stages. Its robust design and high thermal tolerance make it ideal for demanding environments.
4. Are TO-92 transistors suitable for industrial applications?
TO-92 transistors are not ideal for industrial applications. Their limited power-handling capacity and thermal performance restrict them to low-power tasks in consumer electronics, such as remote controls and sensors.
5. How do engineers decide between TO-66 and TO-92 transistors?
Engineers evaluate factors like power requirements, thermal demands, and physical constraints. TO-66 suits high-power, heat-intensive applications, while TO-92 works best in compact, low-power designs.
Note: Always verify voltage, current, and thermal ratings before selecting a transistor.
See Also
Three Key Benefits of XCF01SVOG20C in Automation
Three Effective Methods for Integrating MC9S12XET512VAG
Comparing STM32F401VCT6 and STR750FV2T6 for Medical Devices
CALL US DIRECTLY
(+86)755-82724686
RM2508,BlockA,JiaheHuaqiangBuilding,ShenNanMiddleRd,Futian District,Shenzhen,518031,CN
www.keepboomingtech.com sales@keepboomingtech.com
