Trump’s executive order for the U.S. Investment Accelerator is reshaping semiconductor manufacturing. The CHIPS Act now aims to attract funding and boost U.S. production. Currently, the U.S. produces only 12% of the world’s semiconductors. The global market for semiconductors is projected to grow by 16.3% this year. The government is allocating $52 billion toward research and the production of semiconductors. This investment is designed to reduce U.S. reliance on foreign supplies. Companies, including semiconductor devices distributors, manufacturers, and researchers, stand to benefit from these initiatives. These efforts could significantly transform the future of the industry.
Key Takeaways
-
The CHIPS Act plans to grow U.S. chip production with $52 billion for research and factories.
-
The U.S. Investment Accelerator pushes private funding and makes chip-making easier.
-
New money supports STEM learning and job training to build skilled workers.
-
The CHIPS Act lowers dependence on foreign chips, making U.S. supply chains safer.
-
Even with its promise, the CHIPS Act has problems like delays and trade issues to fix.
Understanding the CHIPS Act
Goals of the Original CHIPS Act
The CHIPS and Science Act of 2022 was created to help the U.S. lead in making semiconductors. It aimed to rely less on other countries, especially China, by producing more chips at home and funding research. The Department of Commerce added rules to stop China from getting advanced chip technology. These rules included checking investments and stopping experts from helping foreign companies.
The original CHIPS Act had these main goals:
|
Goal |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Make chips in the U.S. |
Increase the U.S.’s share of top-level chips, which is now 0%. |
|
Build steady supply |
Make sure there are enough older chips available. |
|
Fund research |
Create new and better chip technology in the U.S. |
|
Create jobs |
Add thousands of factory jobs and many construction jobs, focusing on diversity. |
These goals show the government’s plan to grow the chip industry and keep the economy strong.
Role of the CHIPS Act in U.S. Semiconductor Manufacturing
The CHIPS Act has been key in changing how chips are made in the U.S. With $52 billion in funding, it has encouraged companies to build and grow factories in America. This funding also helps fix supply chain problems, making chip supplies more reliable for industries.
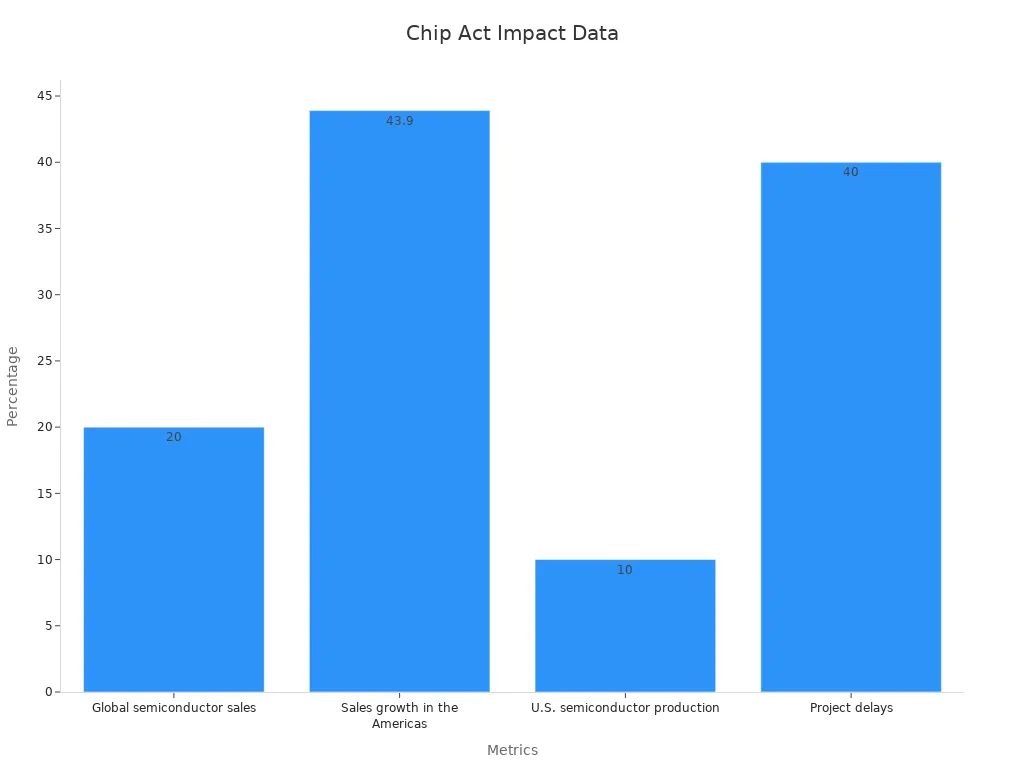
Recent numbers show how the CHIPS Act has helped the chip industry:
|
Metric |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Global chip sales |
Went up by over 20% in August |
|
Chip sales in the Americas |
Grew 43.9% compared to last year |
|
U.S. chip production |
Now 10% of global production (was 37% in 1990) |
|
Delays in big projects |
40% of announced projects faced delays |
The CHIPS Act also led to the Building Chips in America Act 2023. This law speeds up chip projects by skipping some reviews. Supporters say this will make the CHIPS Act even better for the economy and security.
The CHIPS Act projects show why government help is important for the chip industry. By solving supply issues and encouraging new ideas, the act helps the U.S. stay a leader in chip technology.
Trump’s Executive Order and the Investment Accelerator
Creation of the U.S. Investment Accelerator
Trump’s executive order started the U.S. Investment Accelerator. This is an important part of the CHIPS Act. The March 31st order set up this program to manage the CHIPS Program and support research teamwork. A new office in the Commerce Department was created to make processes easier and attract investments in making semiconductors. Another order on March 20th added federal help for critical minerals, giving more resources for U.S. production.
The Investment Accelerator is expected to change the semiconductor industry. It offers rewards to bring in private money and helps businesses work with research groups. Even with high interest rates, U.S. businesses invested $430 billion, showing strong economic growth. This shows how the Investment Accelerator could boost demand and grow the economy. But some experts worry that other policies might hurt the CHIPS Act and harm the U.S. economy.
|
Executive Order |
Description |
|---|---|
|
March 31st EO |
Creates the Investment Accelerator office for the CHIPS Program. |
|
March 20th EO |
Adds federal help for critical mineral projects. |
Improving Oversight and Making Better Deals
The U.S. Investment Accelerator works to improve oversight and make better deals under the CHIPS Act. It actively negotiates deals and speeds up investments. By removing certain labor rules, the government allows nonunion contractors to join projects. This opens up more chances for different groups to work on semiconductor projects.
Better oversight ensures money is used wisely and clearly. Financial studies show that the financial accelerator increases investment during demand spikes. While its effect on production changes is small, it plays a big role in boosting investments. These steps aim to build a strong and creative semiconductor industry while managing risks.
Note: The U.S. Investment Accelerator is a key change in the CHIPS Act, focusing on rewards, oversight, and teamwork to grow U.S. semiconductor production.
Changes in Funding and Regulatory Processes
Adjustments to Funding Allocation
Trump’s updates to the CHIPS Act funding focus on fixing key problems in making chips and training workers. The new plan gives $13 billion over five years for STEM education and job training. This means $2.6 billion will be spent each year. The money helps train skilled workers needed for the chip industry. For comparison, Title 1 of the Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act gave $3.2 billion in 2022, but only a small part went to training. Now, the CHIPS Act sets aside $2.8 billion just for STEM education, showing how important learning is for making better chips.
The act also puts $50 billion into the chip industry for research, development, and production. This change shows a new focus in government spending, matching the Biden administration’s 2021 Regulatory Plan. This plan supports fairness, health, and economic recovery, making sure the money helps society as a whole. These changes show the government’s promise to support new ideas and depend less on foreign chips.
Streamlining Regulatory Oversight
Trump’s executive order makes rules simpler so companies can get federal money and start chip projects faster. The idea of agile regulation is key here. It means learning and adjusting quickly to solve problems in industries like chip-making. A new approval system combines permissions under fewer agencies, cutting down delays and making oversight easier.
Right now, companies need approvals from many agencies, which slows things down. The new system puts all approvals in one place, so projects can start sooner. This plan matches the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, which focuses on fixing infrastructure and creating jobs. By simplifying rules, the government makes sure money is used wisely and helps the chip industry grow faster.
Note: These funding and rule changes show a strong push to grow the U.S. chip industry. By training workers and making processes easier, the updated CHIPS Act helps the U.S. lead in chip-making.
Impacts on Semiconductor Manufacturing
Boosting Domestic Production
The CHIPS Act is helping the U.S. make more microchips. It provides $50 billion for research and production. This money strengthens the U.S. in the global chip market. Investments have already increased because of this act. For example, semiconductor companies leased 33% more property since August 2022. Office space leases grew from 572,525 square feet in 2021 to 1.51 million square feet in 2022. These numbers show rising interest in U.S. chip factories.
The act also supports new ideas and stronger supply chains. It encourages teamwork between private companies and research groups. This helps the U.S. stay ahead in making advanced chips. By 2024, chip manufacturing investments are expected to grow 85% compared to 2019. This will further increase U.S. chip production.
Note: The CHIPS Act is a big change in U.S. chip policy. It helps the U.S. lead in technology and depend less on foreign suppliers.
Challenges in Implementation
The CHIPS Act has great potential but also faces problems. Focusing only on U.S. production could hurt the supply of advanced chips. Relying on national sources might cause shortages, higher costs, and lower-quality products. Companies may also face delays in launching new products due to supply chain issues.
Trade fights with other countries are another concern. Tensions, especially with China, could block the flow of materials worldwide. Making chips is very complex and often crosses over 70 borders. This adds to the challenges of putting the act into action.
Tip: Solving these problems needs teamwork between the government and chip companies.
Effects on Global Supply Chains
The CHIPS Act focuses on making chips in the U.S., which affects global supply chains. The U.S., Europe, and Japan make chip equipment. Taiwan and South Korea lead in advanced chip production. China handles assembly and testing. This shows how connected the global chip industry is.
Export limits and trade issues have already slowed China’s chipmaking. Natural disasters and sudden demand spikes also create risks. But the CHIPS Act aims to reduce these problems by focusing on U.S. production. This could make the chip supply chain more stable.
Callout: A smart plan is needed to reduce risks while encouraging growth and new ideas in the chip industry.
Implications for the U.S. Economy and National Security
Strengthening Technological Leadership
The CHIPS Act changes help the U.S. stay a leader in chip technology. It provides $52.7 billion for chip programs, including $39 billion for factories. This funding pushes companies to create new ideas and compete better. U.S. businesses are good at using technology to improve. For example, they rank fourth in using cloud services and lead in ICT adoption. These skills help them make production faster and more efficient.
Important measures like patent filings and R&D spending show the U.S. values innovation. Companies work to launch new products faster and succeed in research projects. These actions grow the economy and keep the U.S. strong in technology. Staying ahead in tech is also important for national security.
Reducing Foreign Dependence
The CHIPS Act lowers risks from relying on foreign chipmakers. Right now, over 75% of chips are made in East Asia. This makes the U.S. vulnerable to supply problems. By focusing on making chips at home, the act builds a safer and steadier supply chain.
Other regions, like Europe, are also working on this issue. The European Chips Act aims to double Europe’s chip production by 2030. Similarly, the U.S. is investing in local factories to reduce risks. This helps the economy and protects against global tensions, especially in Taiwan.
Addressing Potential Risks
The CHIPS Act has benefits but also challenges. Export controls could hurt U.S. companies and slow innovation. Working with allies is key to managing these controls and staying competitive. The U.S. also faces risks from chip shortages. For example, carmakers lost four million vehicles due to chip supply issues. This shows how important chips are for the economy.
A conflict in Taiwan could cost the world $10 trillion in one year. This highlights why investing in chip production and supply chains is crucial. By solving these problems, the CHIPS Act helps the U.S. stay strong and secure in a changing world.
Trump’s executive order brought big changes to the CHIPS Act. The U.S. Investment Accelerator was created to boost chip-making in America. New rules also improve how projects are managed. These updates help grow the economy and encourage new ideas. However, there are challenges in making these plans work. If solved, the act could help the U.S. lead in technology and stay secure.
Note: The CHIPS Act is an important move to rely less on other countries and grow technology.
What is the CHIPS Act, and why does it matter?
The CHIPS Act is a U.S. law to grow chip-making at home. It funds research, factories, and worker training. This helps the U.S. rely less on other countries and stay strong in technology.
How does the U.S. Investment Accelerator help chip production?
The U.S. Investment Accelerator brings in private money and speeds up approvals. It helps companies and researchers work together. This program aims to make chips faster and improve new ideas in the industry.
What problems does the CHIPS Act face?
The CHIPS Act has issues like supply chain delays, trade fights, and high costs. These problems can slow projects and raise expenses. Fixing them needs teamwork between the government and businesses.
How does the CHIPS Act affect global supply chains?
The CHIPS Act focuses on making chips in the U.S., reducing global dependence. While it helps U.S. factories, it might hurt partnerships with countries that make semiconductors.
Why is it important to depend less on foreign chips?
Most chips are made in East Asia, which risks U.S. supply chains. Making more chips at home ensures steady supplies, protects security, and grows the economy.
Tip: Learning about the CHIPS Act shows how it shapes the future of technology and manufacturing.
See Also
Ways Technology Continues To Excel In The Electronics Field
The Role Of MAX8647ETE+T In Improving Smartphone Screens
Ways EP2C50F484I8N FPGA Can Revolutionize Your Projects
Three Key Benefits Of XCF01SVOG20C In Automation
Three Effective Methods For Integrating MC9S12XET512VAG


